Quick Start Guide for Python in VS Code
The Python extension makes Visual Studio Code an excellent Python editor, works on any operating system, and is usable with a variety of Python interpreters.
Get started by installing:
- VS Code
- A Python Interpreter (any actively supported Python version)
- Python extension from the VS Code Marketplace
To further customize VS Code for Python, you can leverage the Python profile template, automatically installing recommended extensions and settings. For Data Science projects, consider using the Data Science profile template.
How to create and open a Python project or file
If you have an existing Python project you wish to work on in VS Code, you can begin by opening your folder or file from the VS Code Welcome page or File Explorer view, or by selecting File > Open Folder (Ctrl+K Ctrl+O) or File > Open File (⌘O (Windows, Linux Ctrl+O)).
You can create a new Python file by selecting New File on the VS Code Welcome page and then selecting Python file, or by navigating to File > New File ().
Tip: If you already have a workspace folder open in VS Code, you can add new files or folders directly into your existing project. You can create new folders and files by using the corresponding New Folder or New File icons on the top level folder in the File Explorer view.
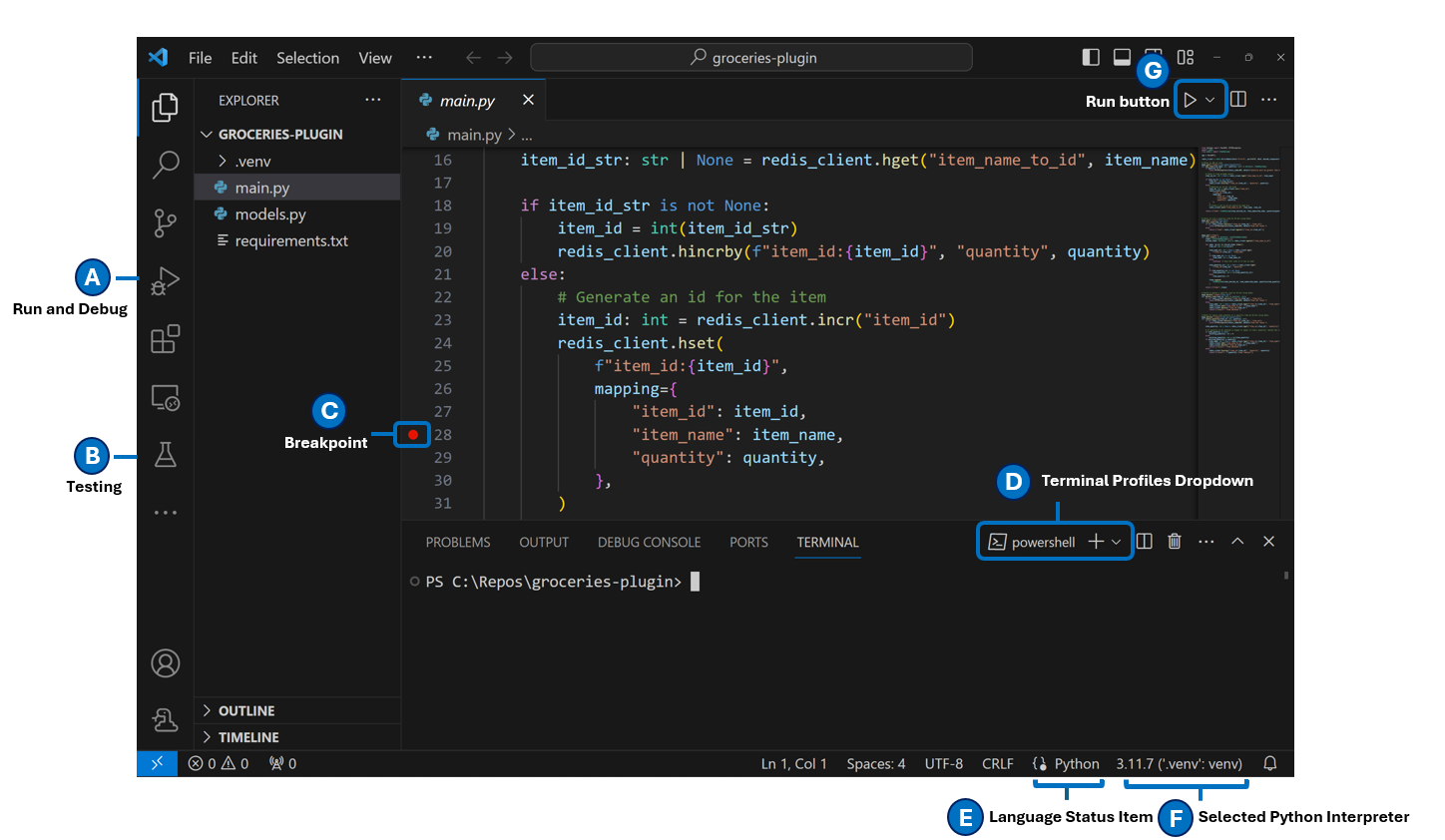
UI tour
When you launch VS Code for the very first time, you will need to install the Python extension to get Python-specific features and UI. Let’s look at the UI after installing the Python extension:
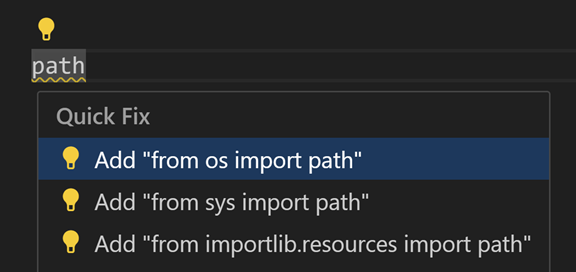
Code Actions
Code Actions (also known as Quick Fixes) are provided to help fix issues when there are warnings in your code. These helpful hints are displayed in the editor left margin as a lightbulb (💡). Select the light bulb to display Code Action options. These Code Action can come from extensions such as Python, Pylance, or VS Code itself. For more information about Code Actions, see Python Quick Fixes.
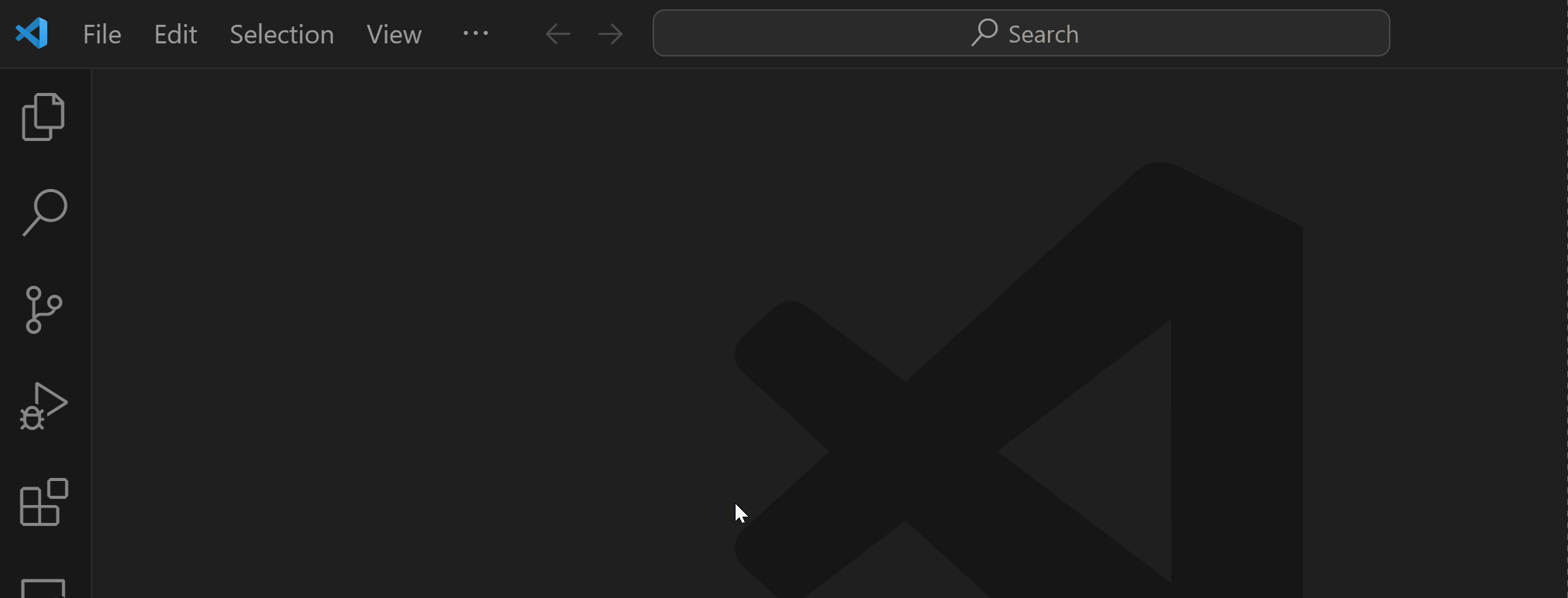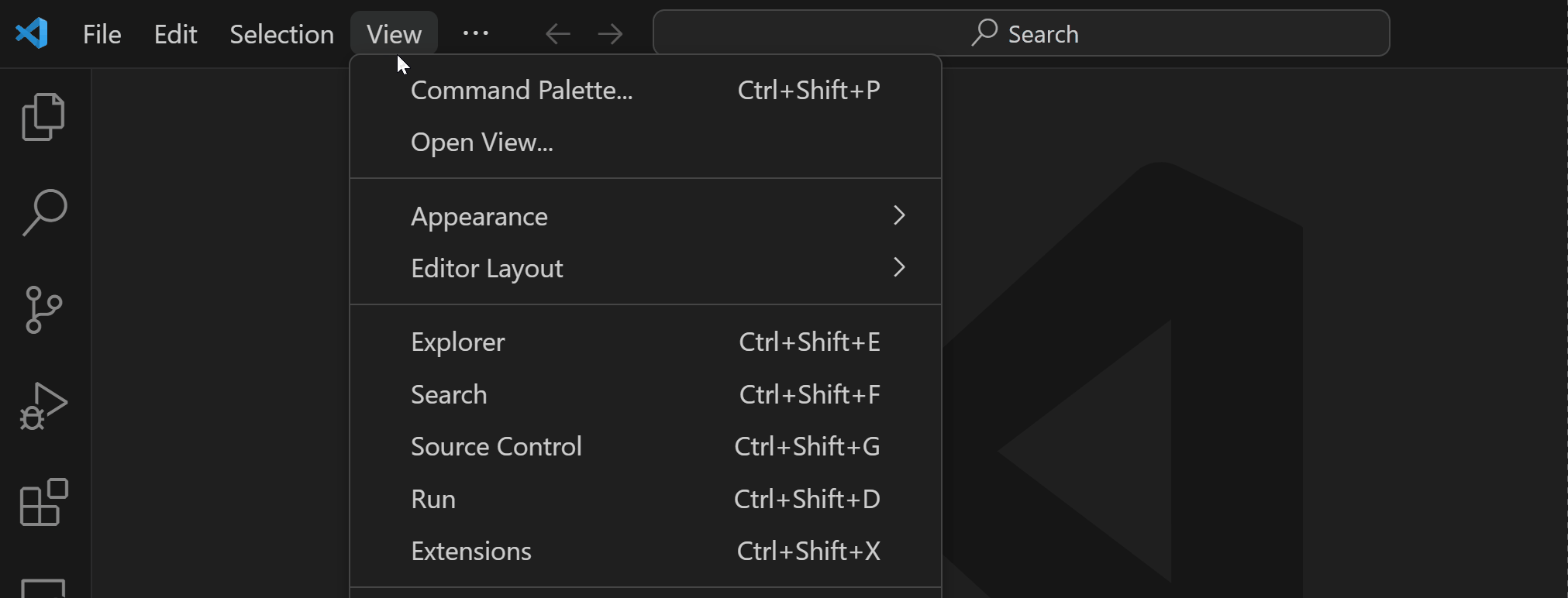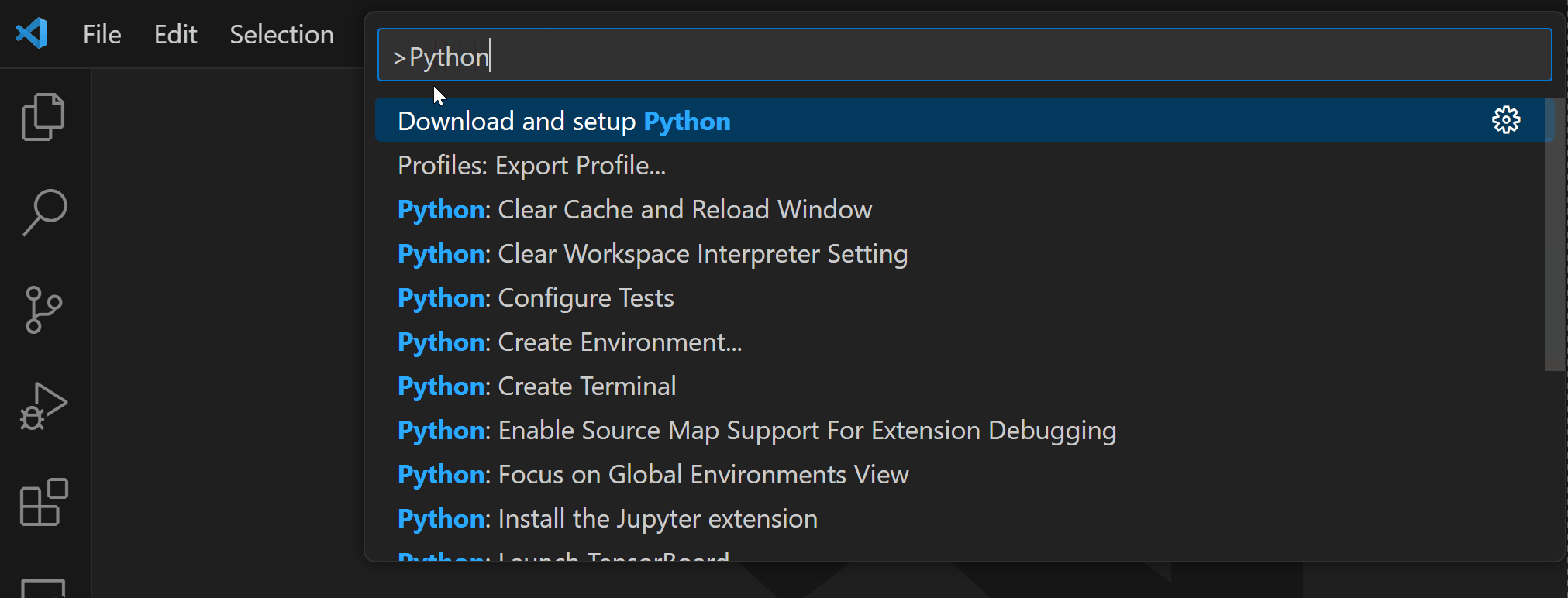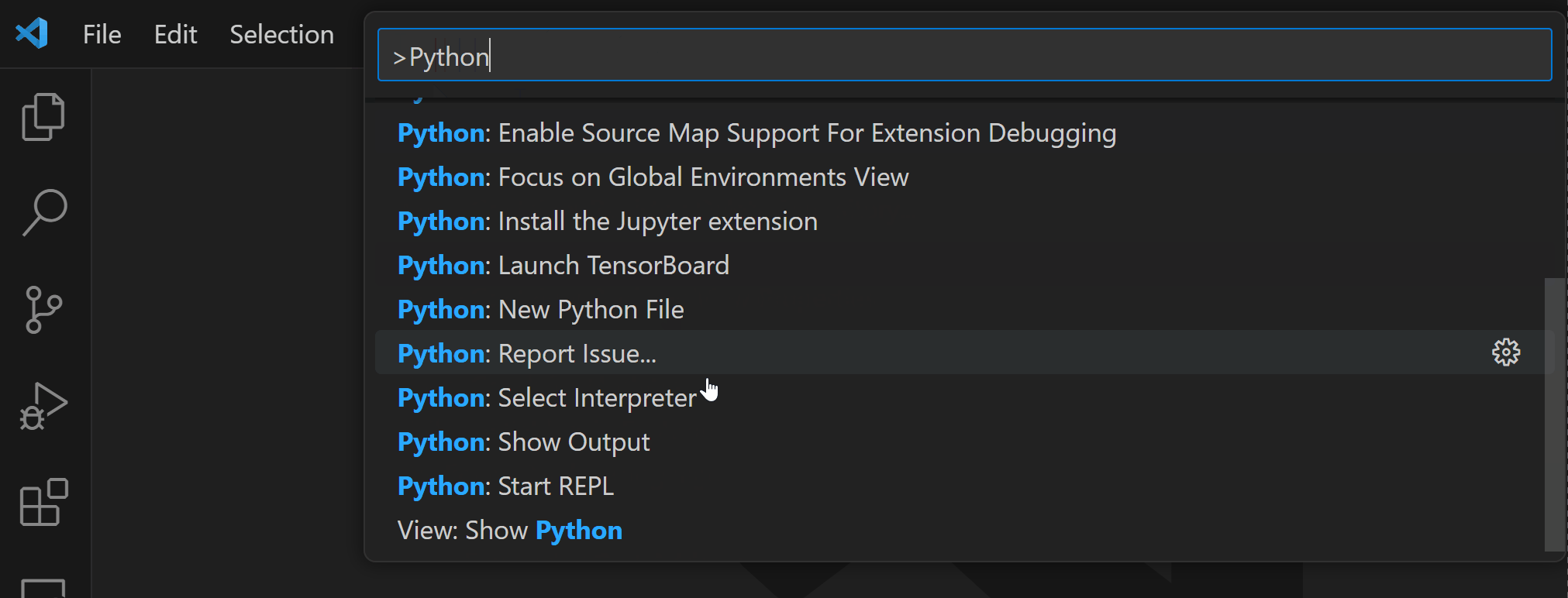
Python commands
Python commands can be accessed through the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)). From the Command Palette, you have access to various features from VS Code and installed extensions. Enter “Python: “ in the Command Palette to find the commands available through the Python extension.
Run, debug, and test
Now that you are more familiar with Python in VS Code, let’s learn how to run, debug, and test your code.
Run
There are a few ways to run Python code in VS Code.
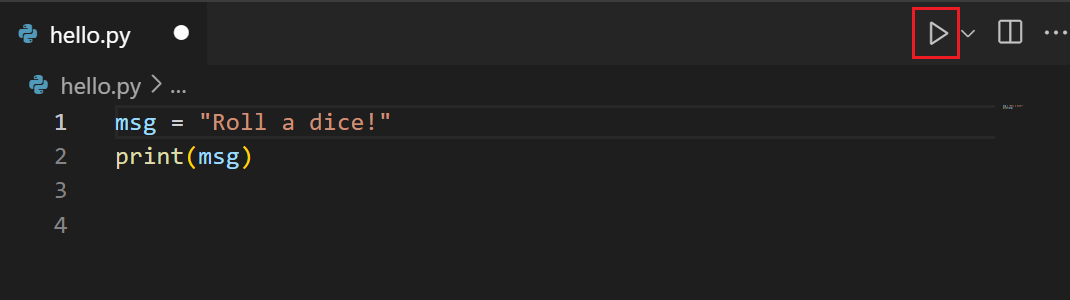
To run the Python script you have open on the editor, select the Run Python File in Terminal play button in the top-right of the editor.
There are also additional ways you can iteratively run snippets of your Python code within VS Code:
- Select one or more lines, then press Shift+Enter or right-click and select Run Selection/Line in Python Terminal. This command is convenient for testing just a part of a file.
- From the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)), select the Python: Start REPL command to open a REPL terminal for the currently selected Python interpreter. In the REPL, you can then enter and run lines of code one at a time.
Debug
The debugger is a helpful tool that allows you to inspect the flow of your code execution and more easily identify errors, as well as explore how your variables and data change as your program is run. You can start debugging by setting a breakpoint in your Python project by clicking in the gutter next to the line you wish to inspect.
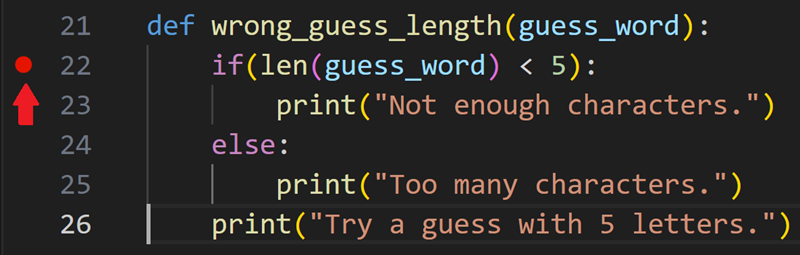
To start debugging, initialize the debugger by pressing F5. Since this is your first time debugging this file, a configuration menu will open allowing you to select the type of application you want to debug. If it's a Python script, you can select Python File.
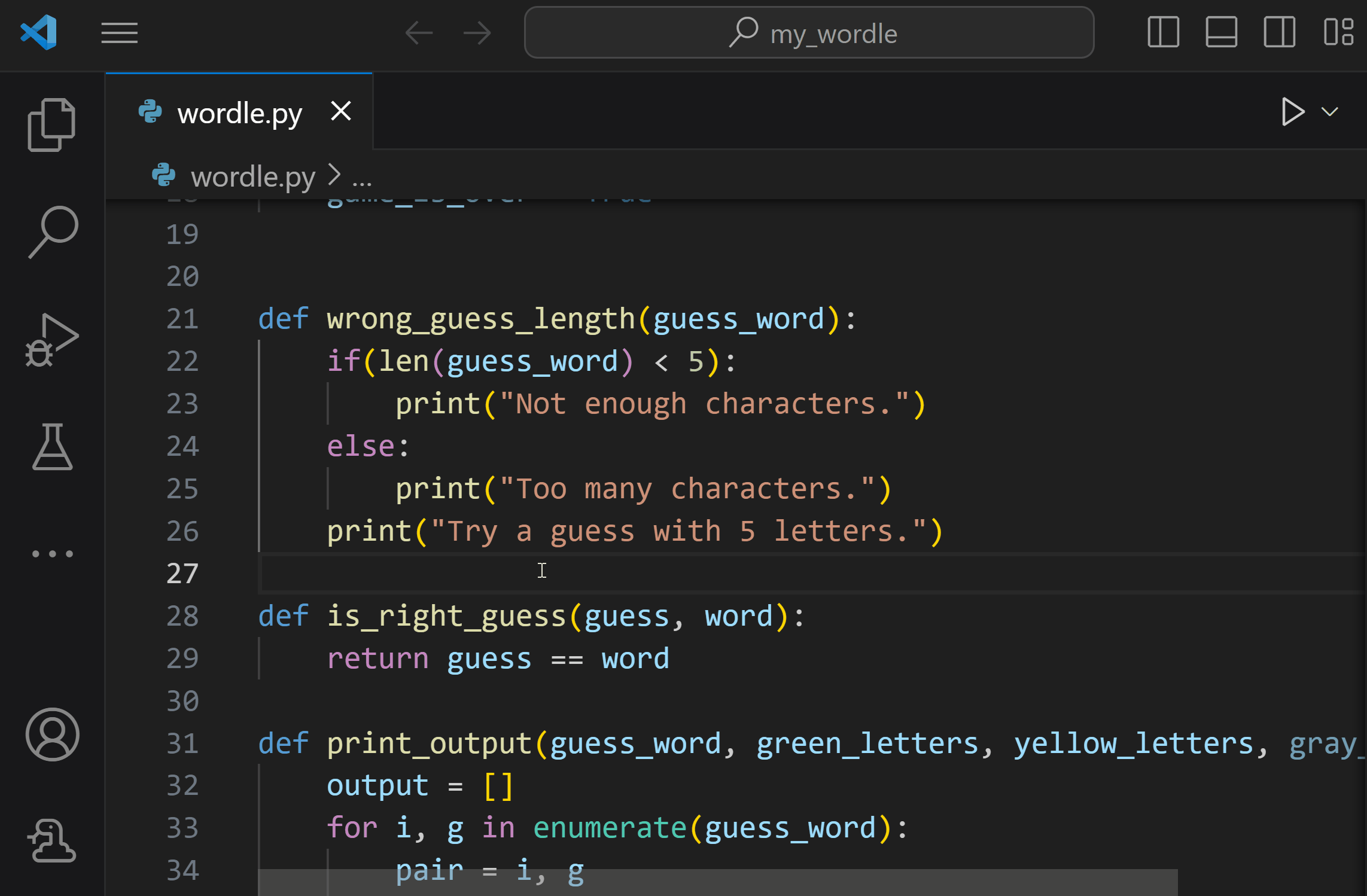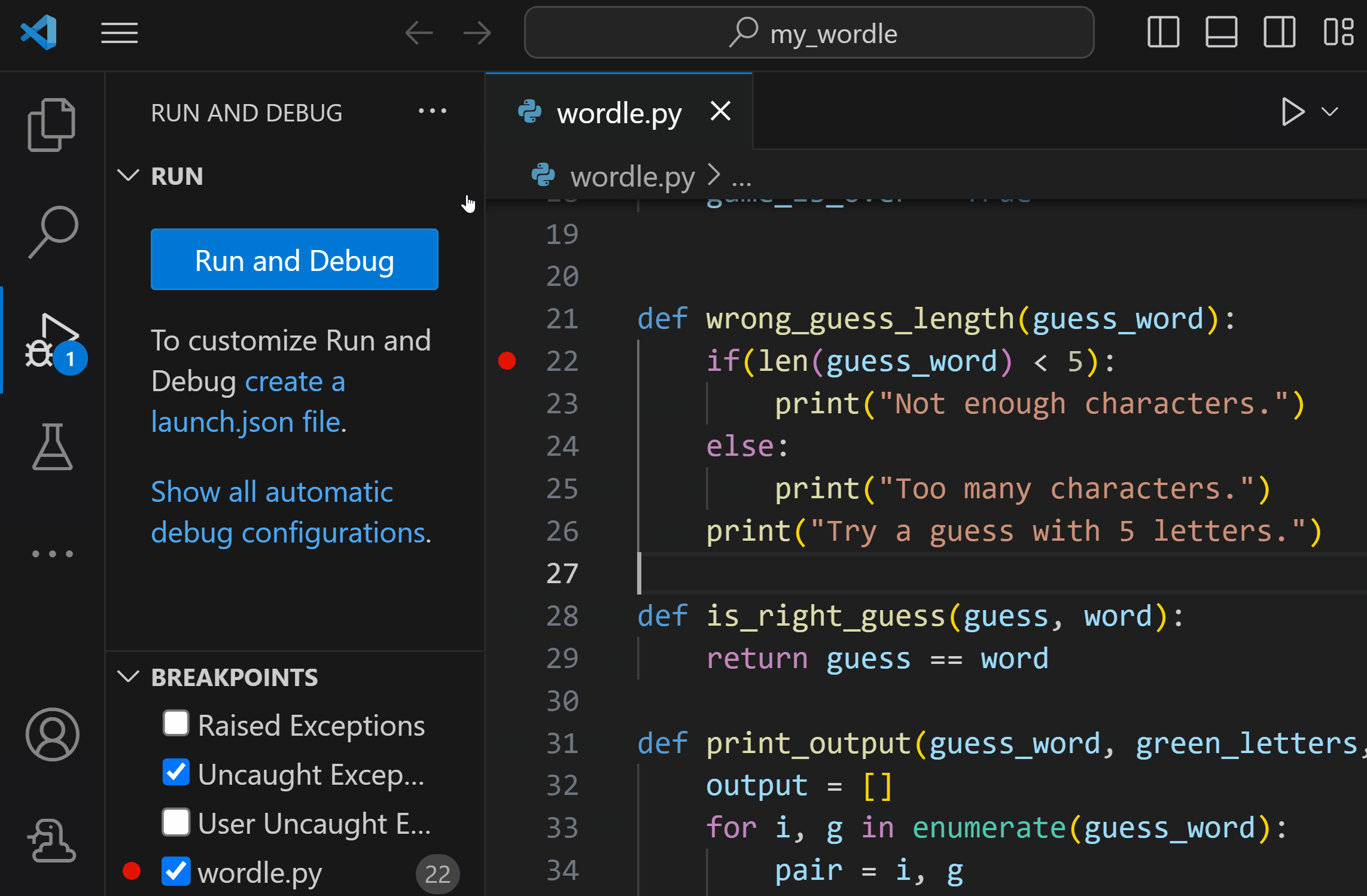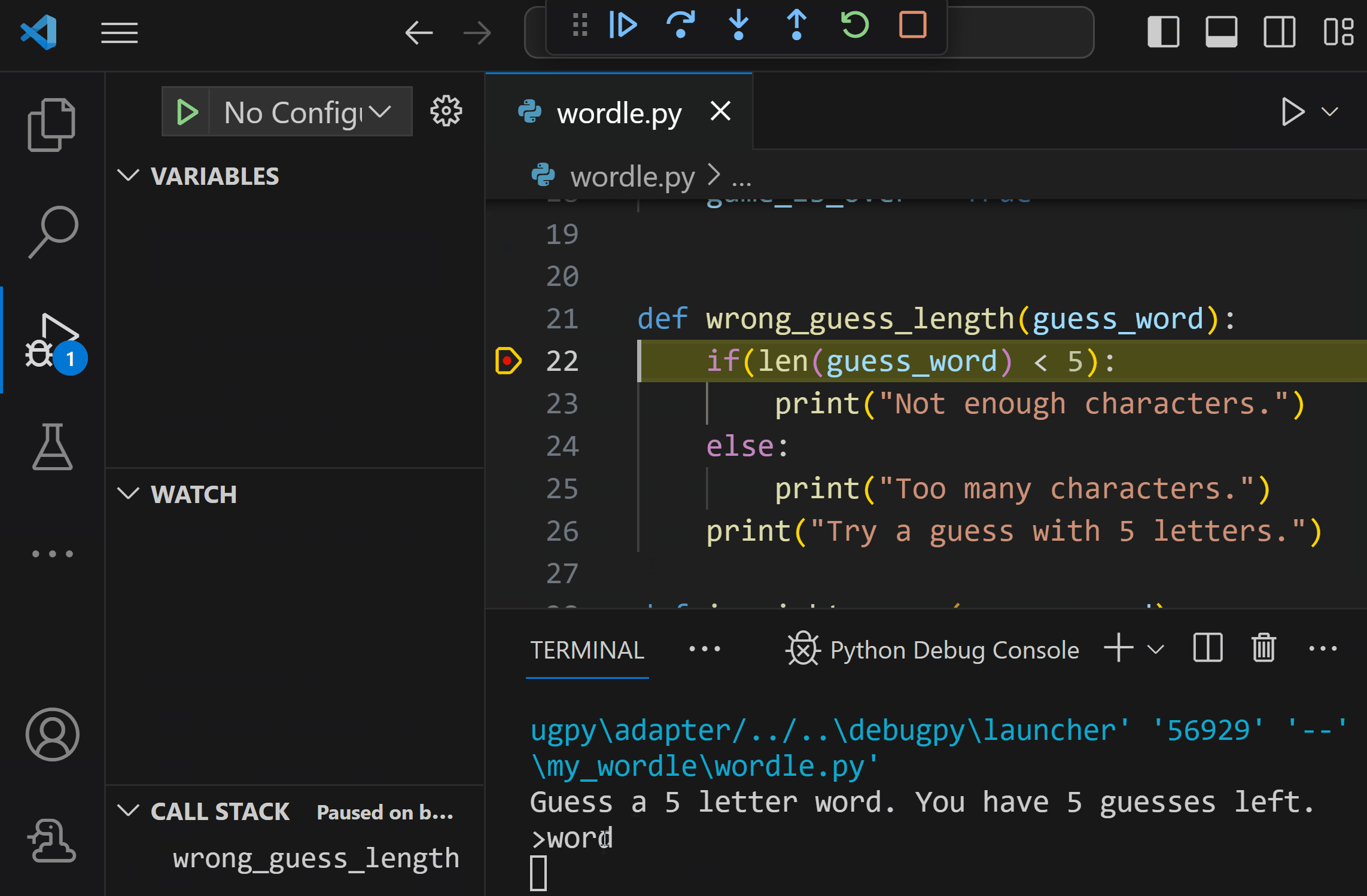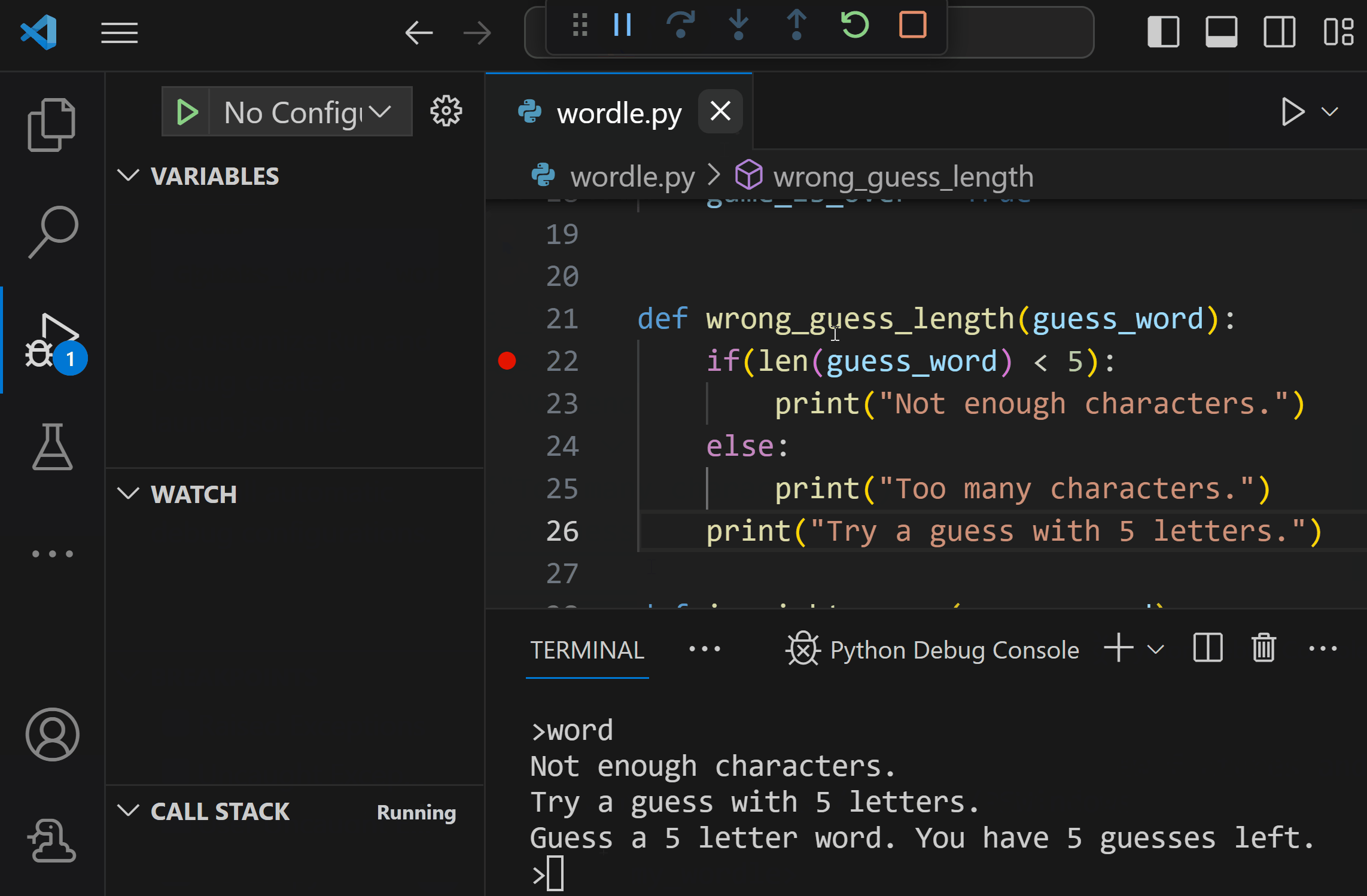
Once your program reaches the breakpoint, it will stop and allow you to track data in the Python Debug console, and progress through your program using the debug toolbar.
For a deeper dive into Python debugging functionality, see Python debugging in VS Code.
Test
The Python extension provides robust testing support for Unittest and pytest.
You can configure Python tests through the Testing view on the Activity Bar by selecting Configure Python Tests and selecting your test framework of choice.
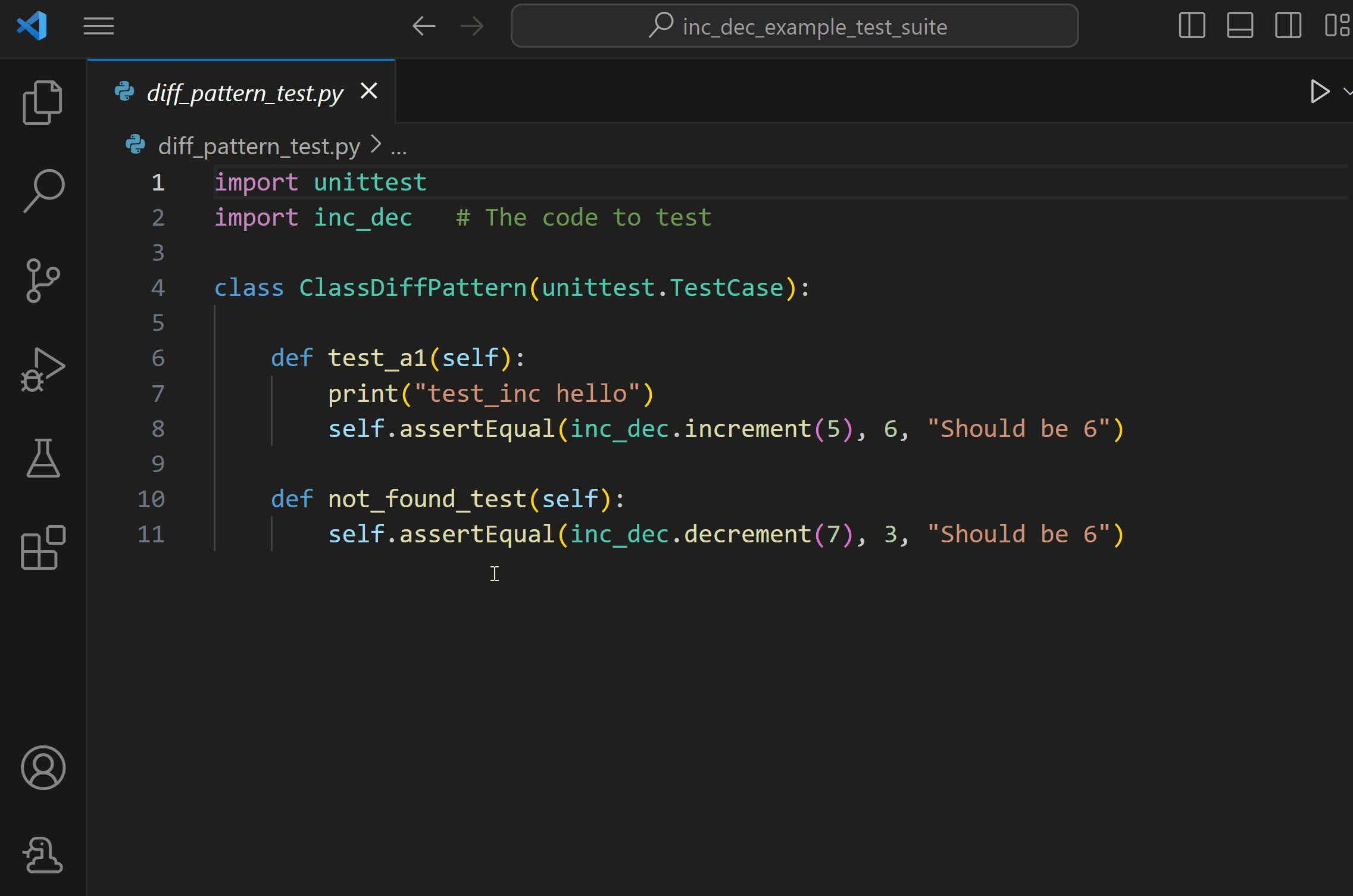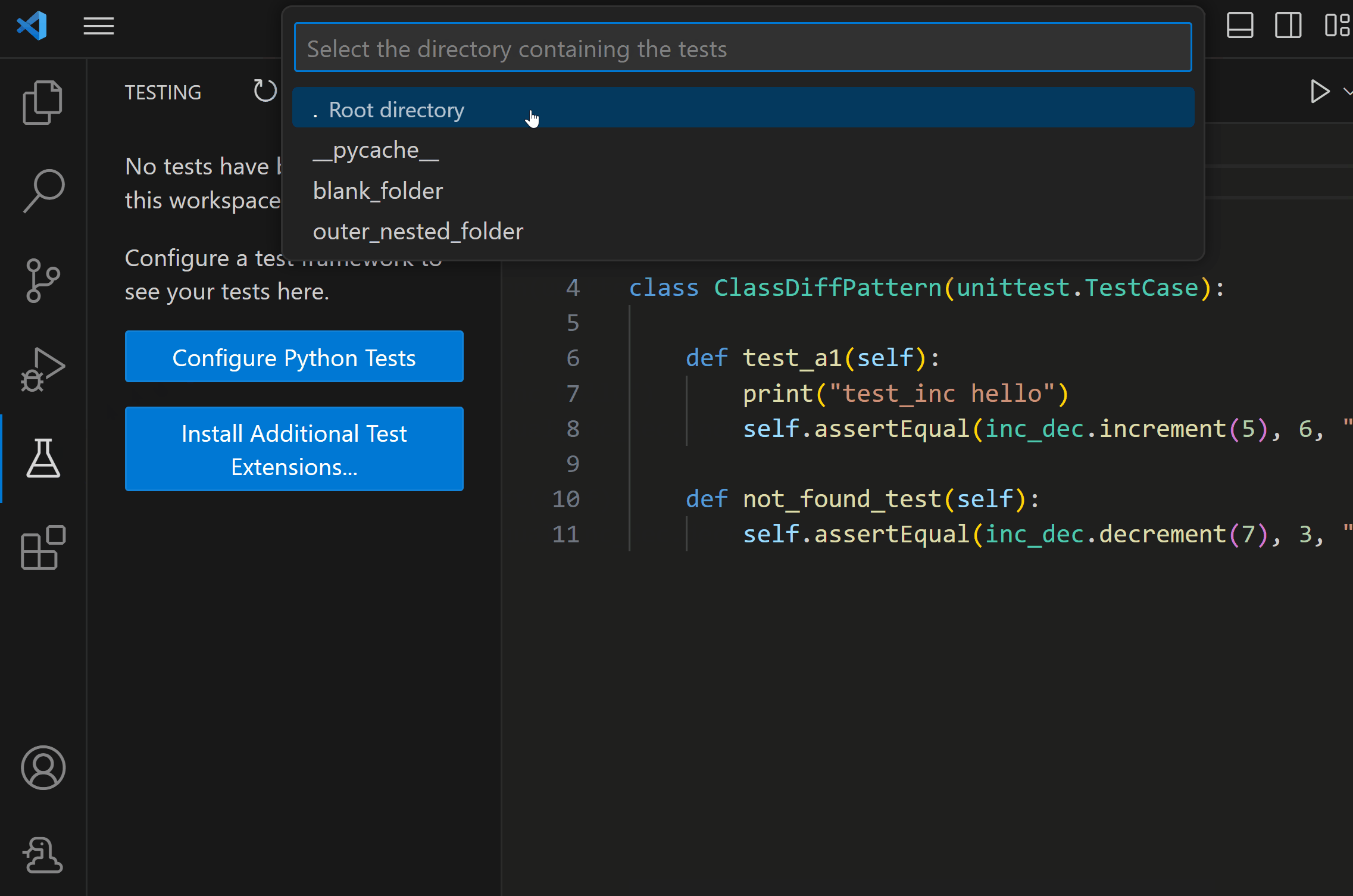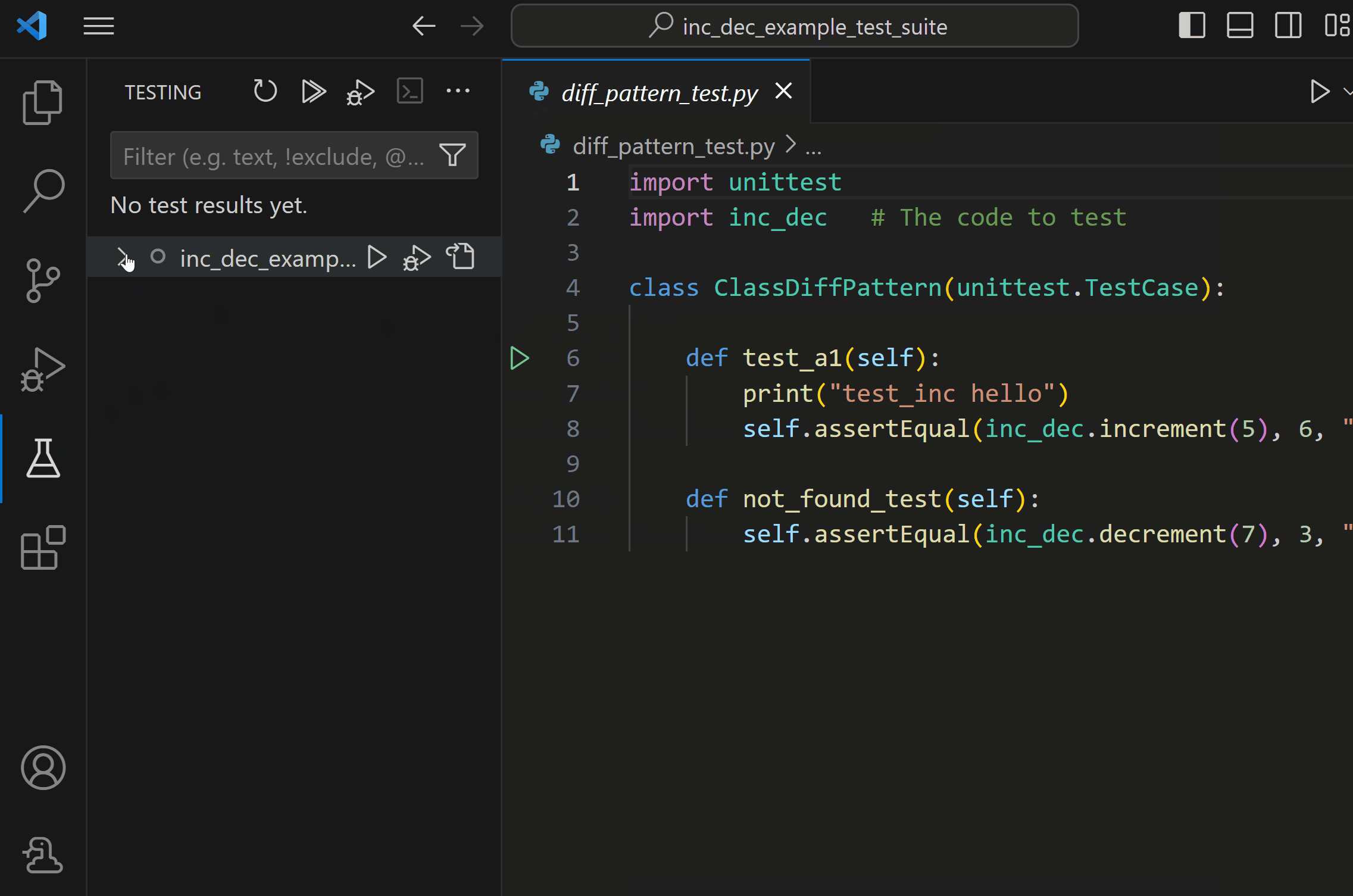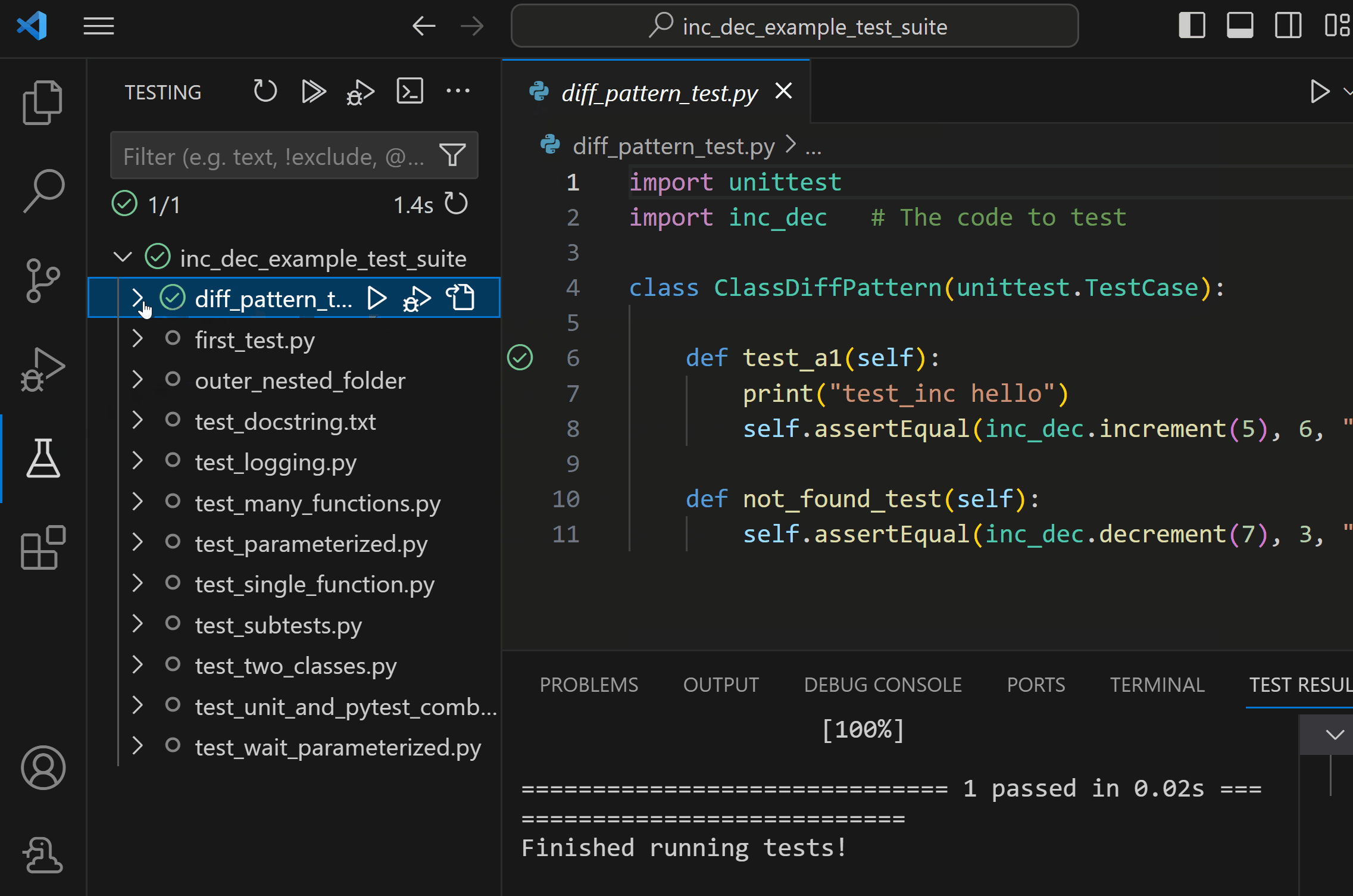
You can also create tests for your Python project, which the Python extension will attempt to discover once your framework of choice is configured. The Python extension also allows you to run and debug your tests in the Testing view and inspect the test run output in the Test Results panel.
For a comprehensive look at testing functionality, see Python testing in VS Code.
Next steps
To learn how to build web apps with popular Python web frameworks, see the following tutorials:
There is much more to explore with Python in Visual Studio Code:
- Python profile template - Create a new profile with a curated set of extensions, settings, and snippets
- Editing code - Learn about autocomplete, IntelliSense, formatting, and refactoring for Python.
- Linting - Enable, configure, and apply a variety of Python linters.
- Debugging - Learn to debug Python both locally and remotely.
- Testing - Configure test environments and discover, run, and debug tests.
- Settings reference - Explore the full range of Python-related settings in VS Code.