Workspace Trust
Visual Studio Code takes security seriously and wants to help you safely browse and edit code no matter the source or original authors. The Workspace Trust feature lets you decide whether code in your project folder can be executed by VS Code and extensions without your explicit approval.
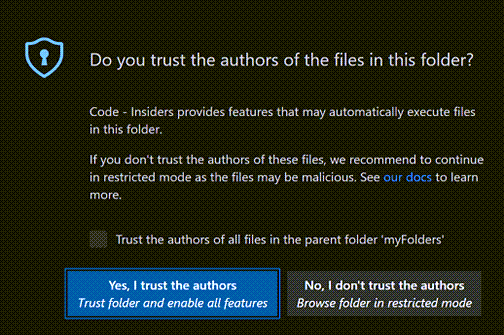
Note: When in doubt, leave a folder in Restricted Mode. You can always enable trust later.
Safe code browsing
It's great that there is so much source code available on public repositories and file shares. No matter the coding task or problem, there is probably already a good solution available somewhere. It is also great that there are so many powerful coding tools available to help you understand, debug, and optimize your code. However, using open-source code and tools does have risks, and you can leave yourself open to malicious code execution and exploits.
Workspace Trust provides an extra layer of security when working with unfamiliar code, by preventing automatic code execution of any code in your workspace if the workspace is open in "Restricted Mode".
The terms "workspace" and "folder" are used widely in the VS Code UI and documentation. You can think of a "workspace" as a folder with extra metadata created and used by VS Code.
Restricted Mode
When prompted by the Workspace Trust dialog, if you choose No, I don't trust the authors, VS Code goes into Restricted Mode to prevent code execution.
The workbench displays a banner at the top with a link to Manage your folder via the Workspace Trust editor. In the Status Bar, you can also see a badge that indicates that the workspace is in Restricted Mode.
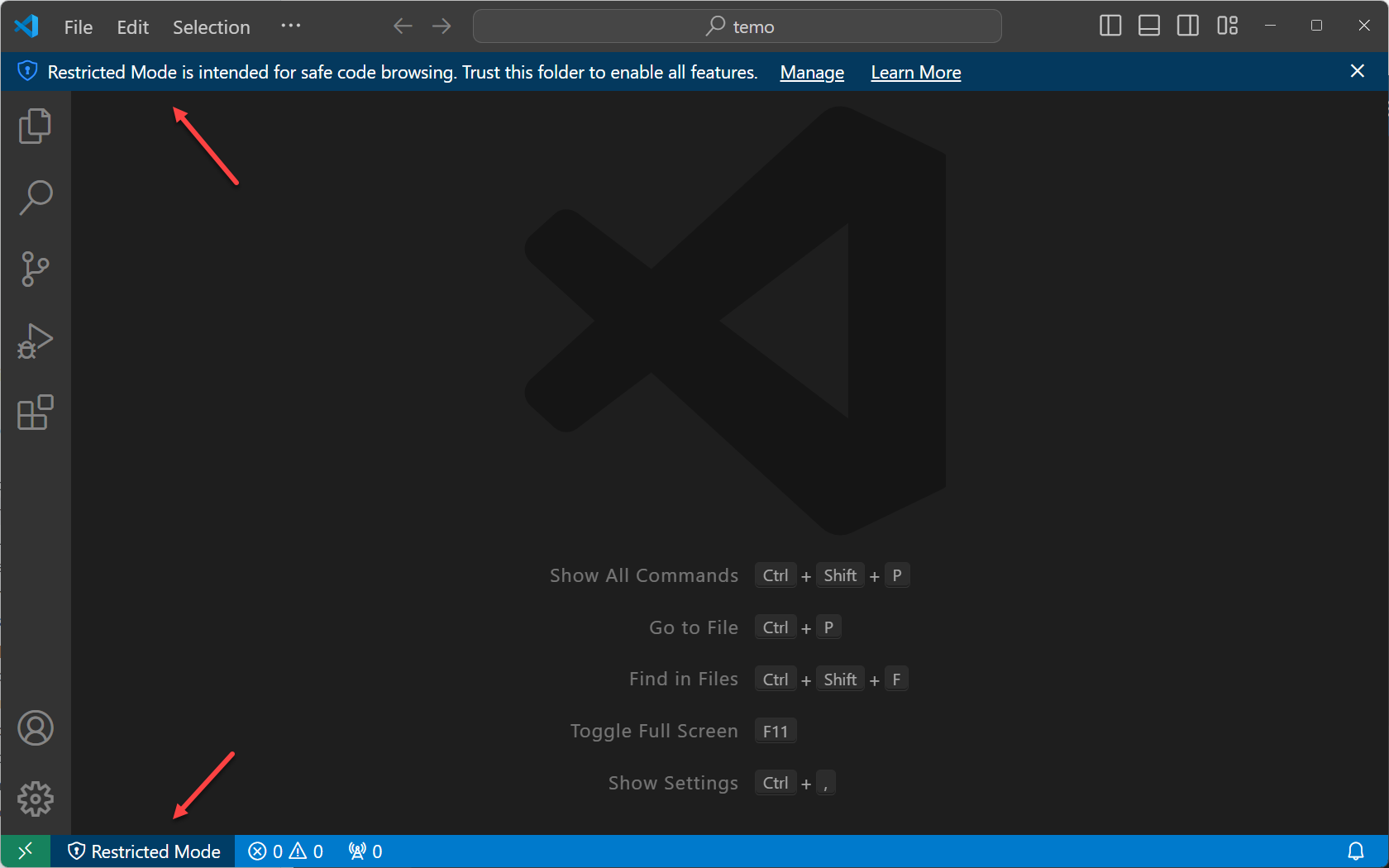
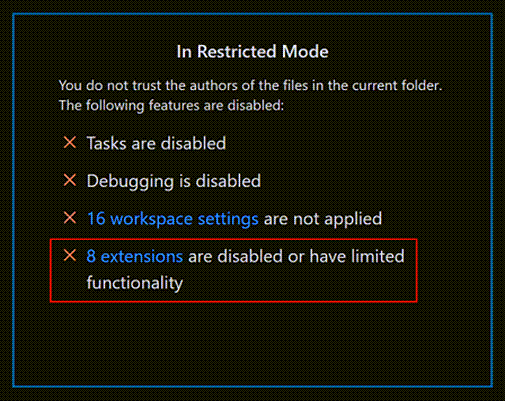
Restricted Mode tries to prevent automatic code execution by disabling or limiting the operation of several VS Code features: AI agents, tasks, debugging, workspace settings, and extensions.
To see the full list of features disabled in Restricted Mode, you can open the Workspace Trust editor via the Manage link in the banner, or by selecting the Restricted Mode badge in the Status Bar. The Workspace Trust editor opens by default in a modal overlay on top of the editor area.
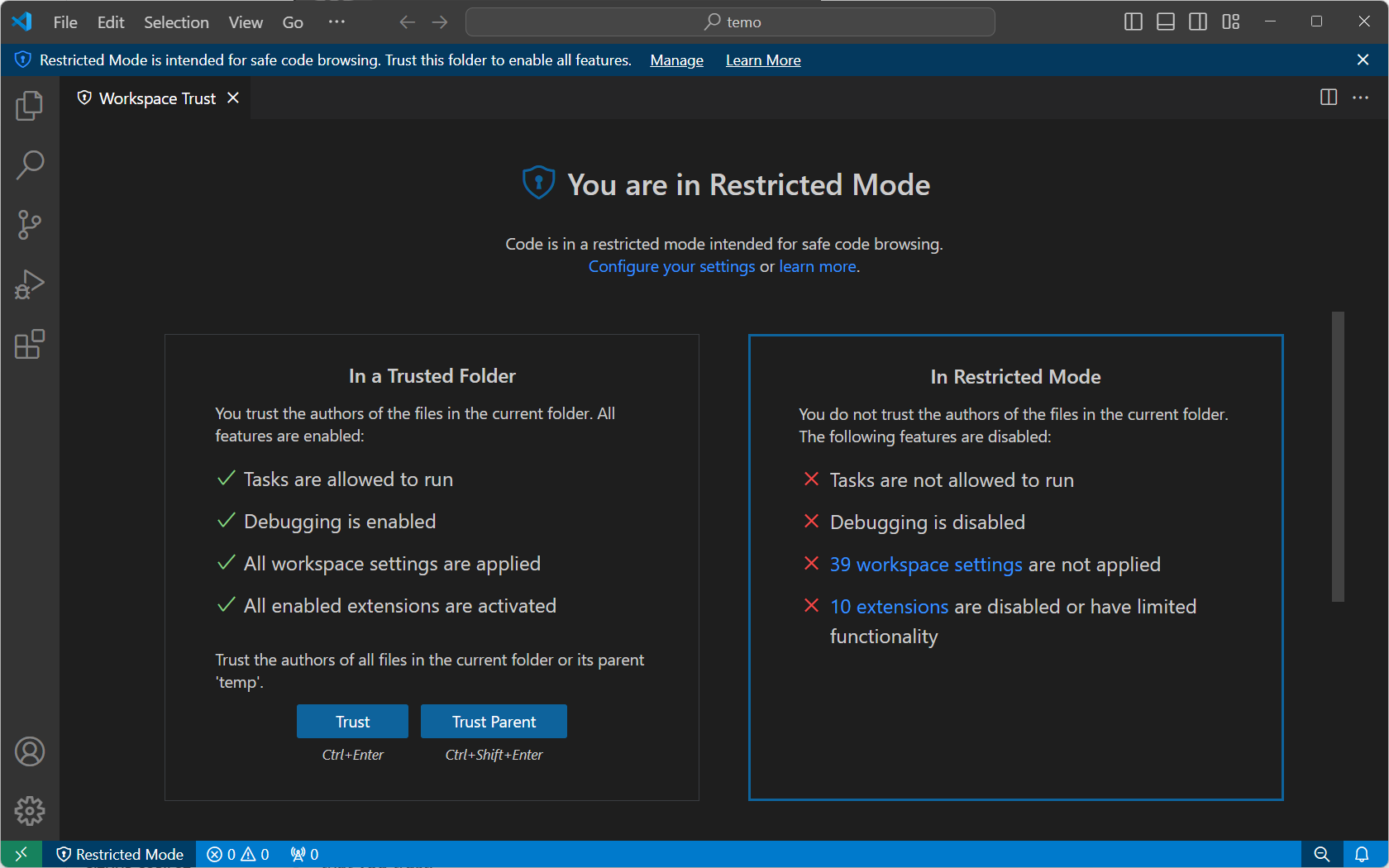
Workspace Trust can't prevent a malicious extension from executing code and ignoring Restricted Mode. You should only install and run extensions that come from a well-known publisher that you trust.
AI agents
When you use AI-powered development features like agents in VS Code, these agents perform actions on your behalf, including making changes to your codebase, running terminal commands, or invoking web requests. Any file could be pulled into the context by using agents and could theoretically result in a prompt injection attack.
Until you've reviewed a project for malicious content, rely on the Workspace Trust boundary and open it in restricted mode. Opening a workspace in restricted mode disables agents in that workspace.
Learn more about AI security considerations when using AI-powered development features in VS Code.
Tasks
VS Code tasks can run scripts and tool binaries. Because task definitions are defined in the workspace .vscode folder, they are part of the committed source code for a repo, and shared to every user of that repo. If someone would create a malicious task, it could be unknowingly run by anyone who cloned that repository.
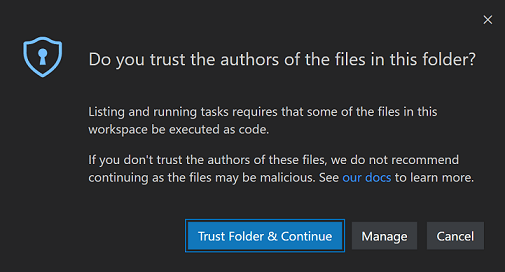
If you try to run or even enumerate tasks (Tasks > Run Task) while in Restricted Mode, VS Code displays a prompt to confirm that you trust the folder and can continue executing the task. If you cancel the dialog, VS Code stays in Restricted Mode.
Debugging
Similar to running a VS Code task, debug extensions can run debugger binaries when launching a debug session. For that reason, debugging is also disabled when a folder is open in Restricted Mode.
If you try to start a debug session (Debug > Start Debugging) while in Restricted Mode, VS Code displays a prompt to confirm that you trust the folder and can continue launching the debugger. If you cancel the dialog, VS Code stays in Restricted Mode, and does not start the debug session.
Workspace settings
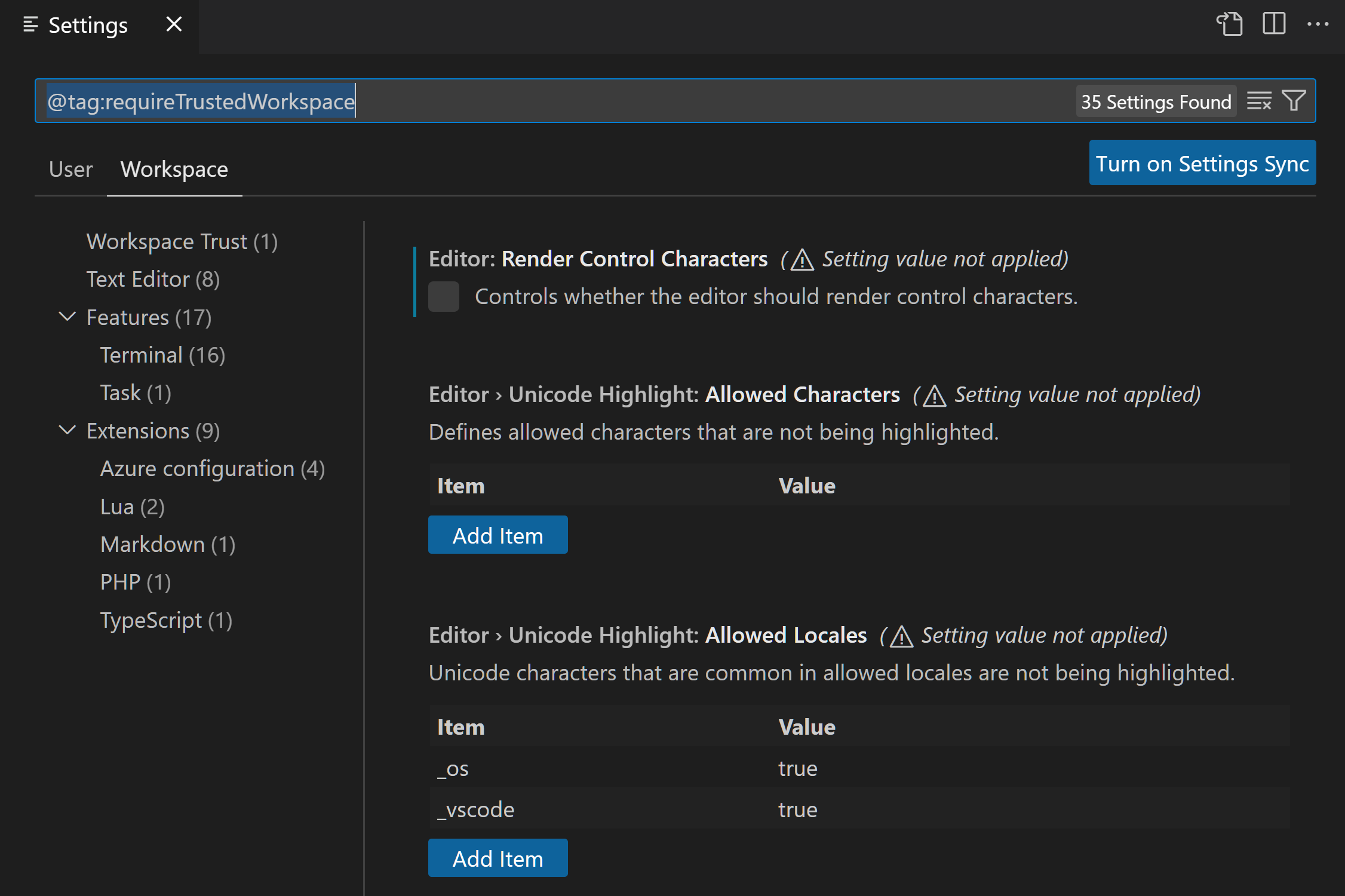
Workspace settings are stored in the .vscode folder at the root of your workspace, and are therefore shared by anyone who clones the workspace repository. Some settings contain paths to executables (for example, linter binaries), which if set to point to malicious code, could cause damage. For this reason, VS Code disables a set of workspace settings when running in Restricted Mode.

In the Workspace Trust editor, select the link for workspace settings that aren't being applied to bring up the Settings editor scoped by the @tag:requireTrustedWorkspace tag.
Extensions
The VS Code extensions ecosystem is incredibly rich and diverse. People have created extensions to help with just about any programming task or editor customization. Some extensions provide full programming language support (IntelliSense, debugging, code analysis), and others let you play music or have virtual pets.
Most extensions run code on your behalf and could potentially do harm. Some extensions have settings that could cause them to act maliciously if configured to run an unexpected executable. For this reason, extensions that have not explicitly opted into Workspace Trust are disabled by default in Restricted Mode.
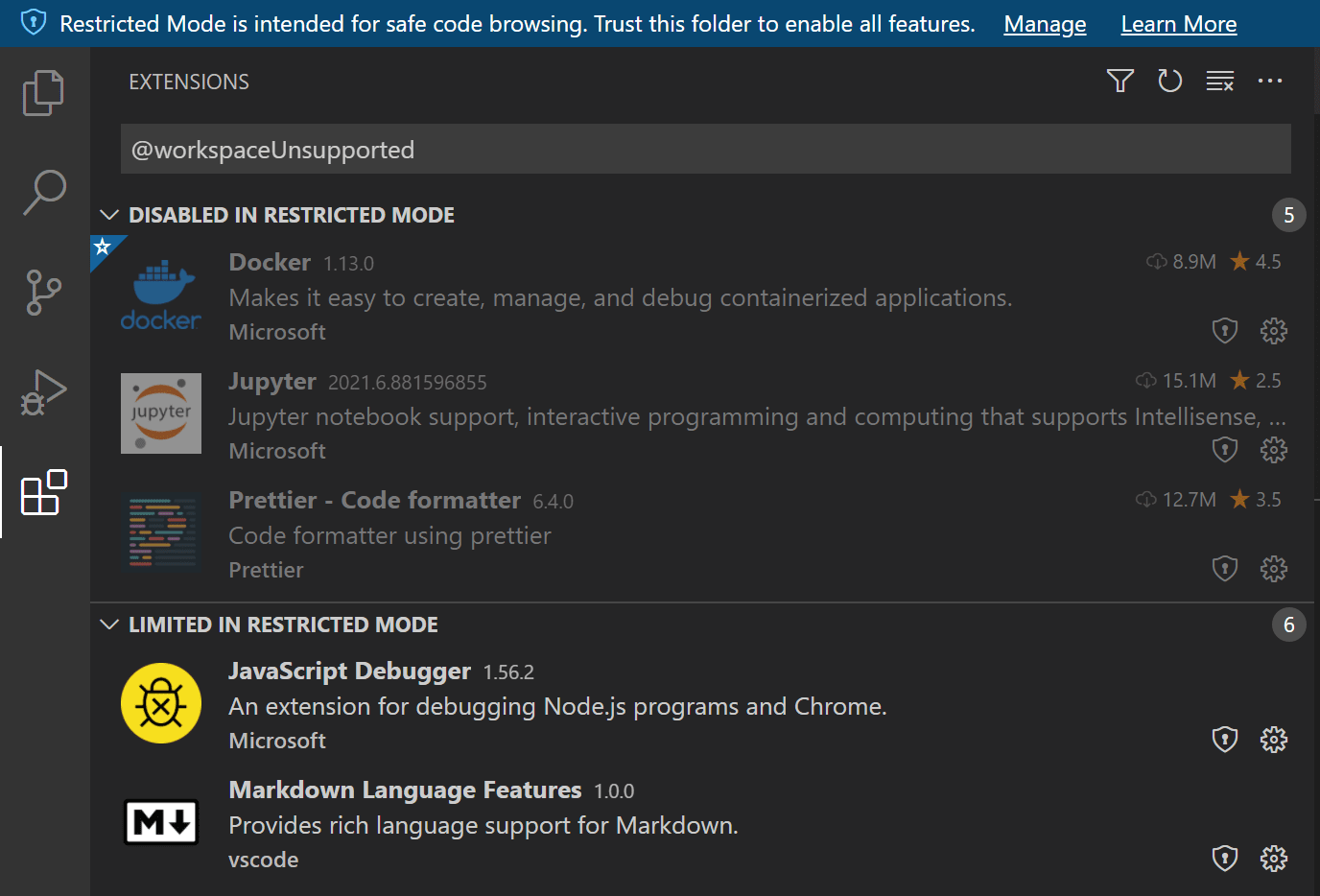
You can review an installed extension's status by selecting the extensions are disabled or have limited functionality link in the Workspace Trust editor, which displays the Extensions view scoped with the @workspaceUnsupported filter.
Extensions that have not opted into Workspace Trust can be either disabled or limited in Restricted Mode.
Disabled in Restricted Mode
Extensions that have either not explicitly indicated that they support running in Restricted Mode are shown in the Disabled in Restricted Mode section. An extension author can also indicate that they never want to be enabled in Restricted Mode if they determine that their extension could be misused by modifications (settings or files) in a workspace.
Limited in Restricted Mode
Extension authors can also evaluate their extensions for possible security vulnerabilities and declare that they have limited support when running in Restricted Mode. This mode means the extension may disable some features or functionality to prevent a possible exploit.
Extensions can add custom text to the Workspace Trust badge in the Extensions view, explaining the limitation when running in an untrusted folder. For example, the VS Code built-in PHP extension limits the use of the php.validate.executablePath setting to trusted folders since overriding this setting could run a malicious program.
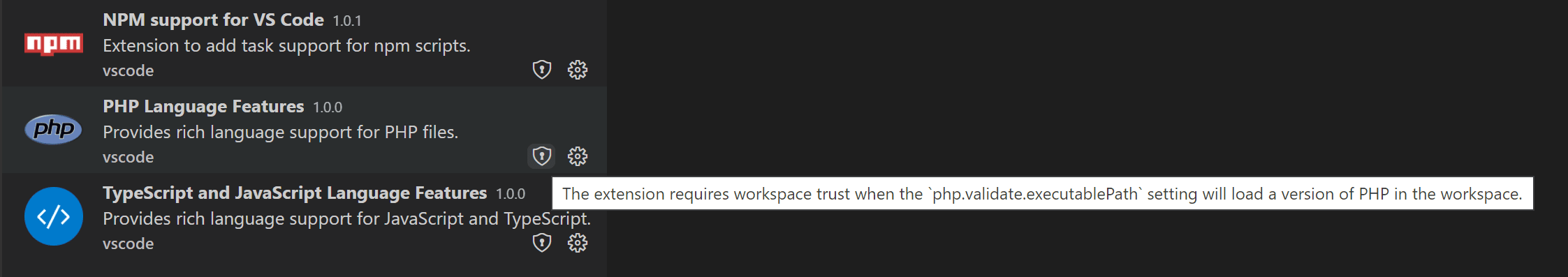
You can override an extension's Workspace Trust support level using the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting, described in the Enabling extensions section below.
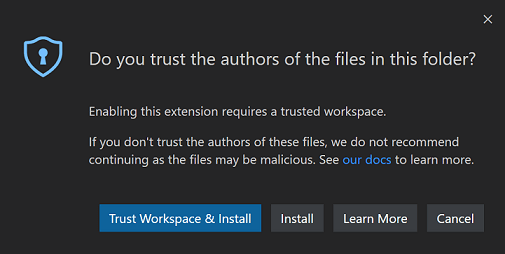
If you try to install an extension in Restricted Mode, you are prompted to either trust the workspace or just install the extension. If the extension doesn't support Workspace Trust, it is installed, but is disabled or runs with limited functionality.
Extension authors can learn how to update their extensions to support Workspace Trust by reading the Workspace Trust Extension Guide.
Trusting a workspace
If you trust the authors and maintainers of a project, you can trust the project's folder on your local machine. For example, it is usually safe to trust repositories from well-known GitHub organizations such as github.com/microsoft or github.com/docker.
When you open a new folder, the initial Workspace Trust prompt enables you to trust that folder and its subfolders.

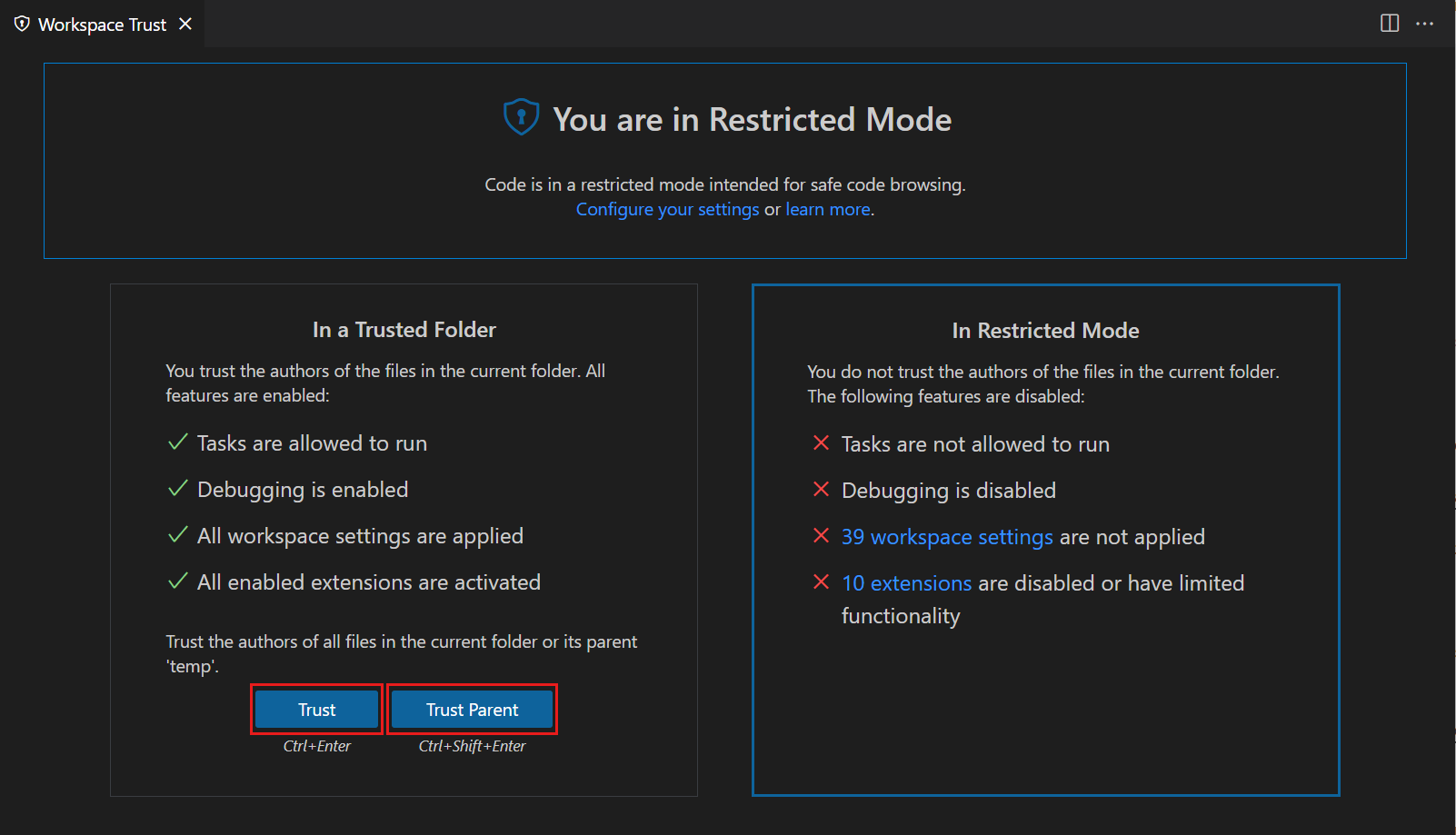
You can also bring up the Workspace Editor and quickly toggle a folder's trusted state by selecting the Trust or Trust Parent button.
There are several ways to bring up the Workspace Trust editor dialog.
When in Restricted Mode:
- Restricted Mode banner Manage link
- Restricted Mode Status Bar item
You can also at any time use:
- Workspaces: Manage Workspace Trust command from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P))
Selecting folders
When you trust a folder, it is added to the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list that is displayed in the Workspace Trust editor.
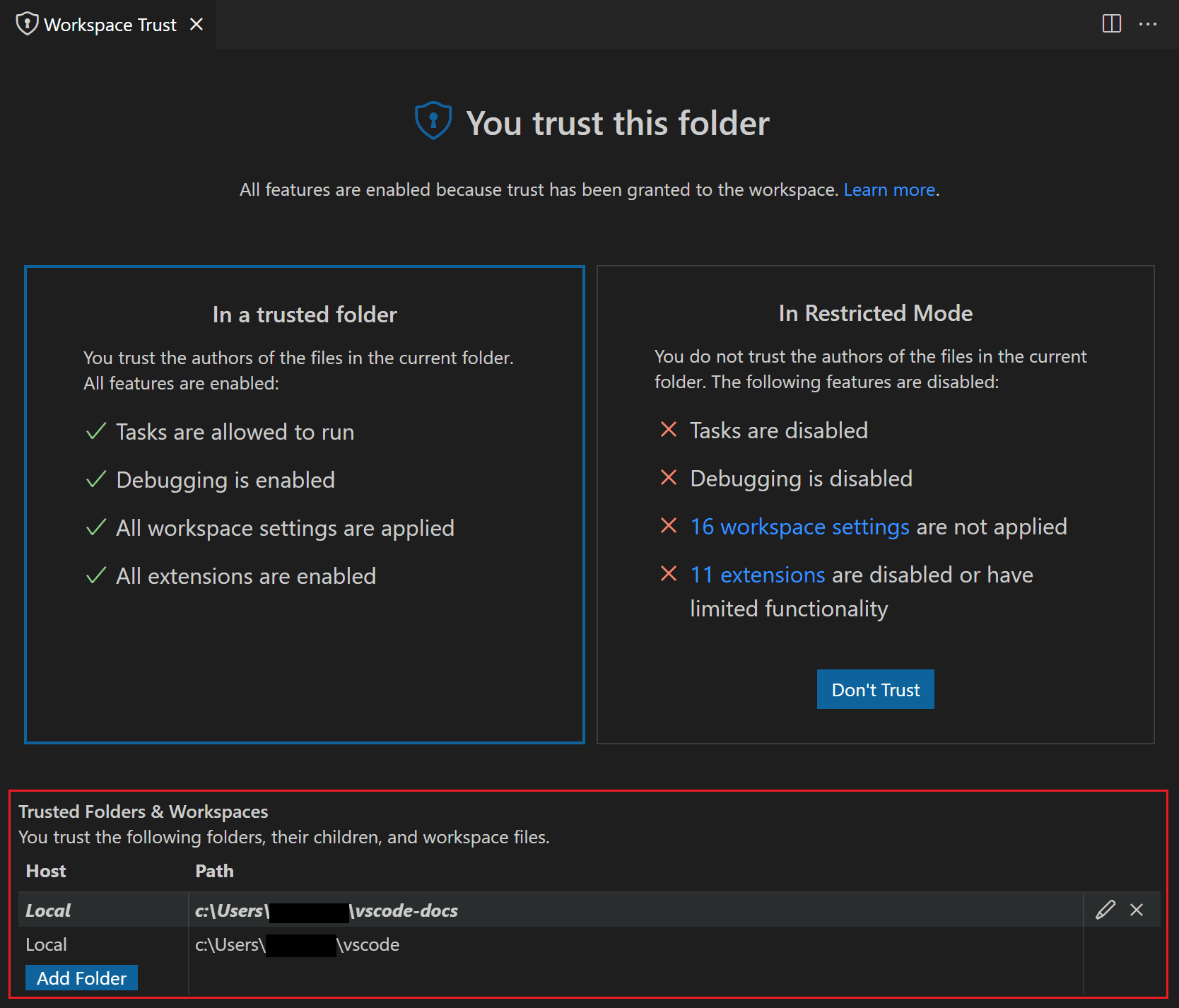
You can manually add, edit, and remove folders from this list to enable or disable workspace trust. The active folder is highlighted in bold in this list.
Selecting a parent folder
When you trust a folder via the Workspace Trust editor, you have the option to also trust the parent folder. This applies trust to the parent folder and all its subfolders.
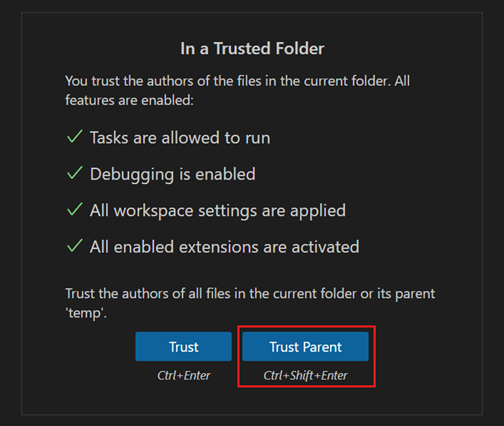
Trusting the parent folder can be helpful if you have many folders with trusted content co-located under one folder.
When you open a subfolder under a trusted parent, you won't see the usual Don't Trust button to put you back in Restricted Mode. Instead, there is text mentioning that your folder is trusted due to another folder.
You can add, modify, and remove a parent folder entry from the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list.
Folder configurations
When you trust a parent folder, all subfolders are trusted, which enables you to control Workspace Trust via a repository's location on disk.
For example, you could put all trusted repos under a "TrustedRepos" parent folder, and unfamiliar repos under another parent folder, such as "ForEvaluation". You would trust the "TrustedRepos" folder, and selectively trust folders under "ForEvaluation".
├── TrustedRepos - Clone trusted repositories under this parent folder
└── ForEvaluation - Clone experimental or unfamiliar repositories under this parent folder
You can also group and set trust on your repositories by grouping them under organization-specific parent folders.
├── github/microsoft - Clone a specific organization's repositories under this parent folder
├── github/{myforks} - Place your forked repositories under this parent folder
└── local - Local un-published repositories
Enabling extensions
What happens if you want to use Restricted Mode but your favorite extension doesn't support Workspace Trust? This can happen if an extension, while useful and functional, isn't being actively maintained and hasn't declared their Workspace Trust support. To handle this scenario, you can override the extension's trust state with the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting.
Be careful with overriding an extension's Workspace Trust support. It's possible that the extension author has a good reason for disabling their extension in Restricted Mode. If in doubt, reach out to the extension author or review recent changelogs to get more context.
In the Settings editor (⌘, (Windows, Linux Ctrl+,)), you can override the Workspace Trust for individual extensions via the Extensions: Support Untrusted Workspaces setting ( extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces ).
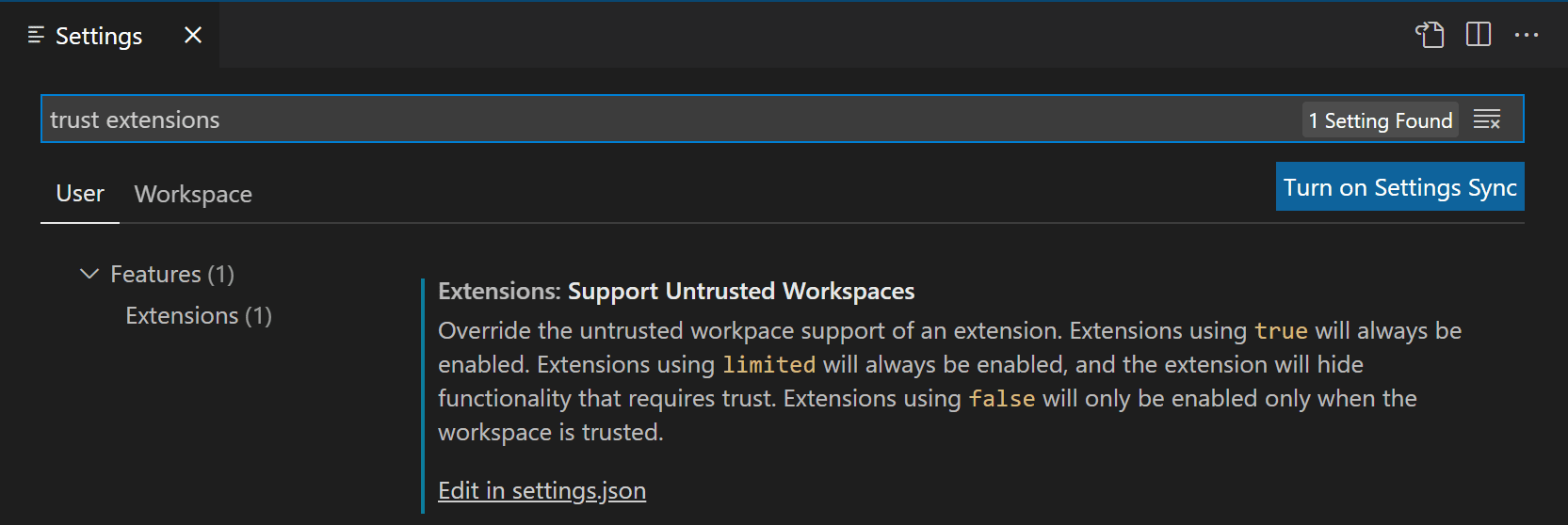
Select the Edit in settings.json link to manage the list of extension IDs and their support status and version. You can select any of your installed extensions via IntelliSense suggestions.
Below you can see a settings.json entry for the Prettier extension.
"extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces": {
"esbenp.prettier-vscode": {
"supported": true,
"version": "6.4.0"
},
},
You can either enable or disable Workspace Trust support with the supported attribute. The version attribute specifies the exact extension version applicable and you can remove the version field if you want to set the state for all versions.
If you'd like to learn more about how extension authors evaluate and determine which features to limit in Restricted Mode, you can read the Workspace Trust Extension Guide.
Opening untrusted files
If you open a file that is located outside of a trusted folder, VS Code detects that the file comes from somewhere outside the folder root and prompts you with the option to continue to open the file or open the file in a new window in Restricted Mode. Opening in Restricted Mode is the safest option and you can always reopen the file in your original VS Code window once you determine the file is trustworthy.
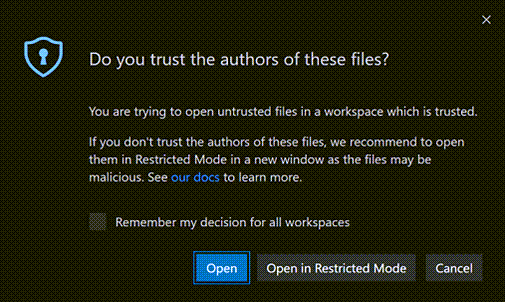
If you would prefer to not be prompted when opening files from outside trusted workspaces, you can set
security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles
to open. You can also set
security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles
to newWindow to always create a new window in Restricted Mode. Checking the Remember my decision for all workspaces option in the untrusted files dialog applies your choice to the
security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles
user setting.
Opening untrusted folders
When working with multi-root workspaces with multiple folders, if you try to add a new folder to a trusted multi-root workspace, you are prompted to decide if you trust the files in that folder or if not, the entire workspace will switch to Restricted Mode.

Empty windows (no open folder)
By default, if you open a new VS Code window (instance) without opening a folder or workspace, VS Code runs the window with full trust. All installed extensions are enabled and you can use the empty window without restrictions.
When you open a file, you are prompted whether you want to open an untrusted file, since there is no folder to parent it.
You can switch an empty window to Restricted Mode by using the Workspace Trust editor (select Workspaces: Manage Workspace Trust in the Command Palette), and then selecting Don't Trust. The empty window remains in Restricted Mode for your current session but reverts back to trusted if you restart or create a new window.
If you want all empty windows to be in Restricted Mode, you can set
security.workspace.trust.emptyWindow
to false.
Settings
Below are the available Workspace Trust settings:
- security.workspace.trust.enabled - Enable Workspace Trust feature. Default is true.
- security.workspace.trust.startupPrompt - Whether to show the Workspace Trust dialog on startup. Default is to only show once per distinct folder or workspace.
- security.workspace.trust.emptyWindow - Whether to always trust an empty window (no open folder). Default is true.
- security.workspace.trust.untrustedFiles - Controls how to handle loose files in a workspace. Default is to prompt.
- extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces - Override extension Workspace Trust declarations. Either true or false.
-
security.workspace.trust.banner
- Controls when the Restricted Mode banner is displayed. Default is
untilDismissed.
Command-line switch
You can disable Workspace Trust via the VS Code command line by passing --disable-workspace-trust. This switch only affects the current session.
Next steps
Learn more at:
- Workspace Trust Extension Guide - Learn how extension authors can support Workspace Trust.
- What is a VS Code "workspace"? - Find out more details about the VS Code "workspace" concept.
- GitHub Repositories extension - Work directly on a repository without cloning the source code to your local machine.
Common questions
Can I still edit my source code in Restricted Mode?
Yes, you can still browse and edit source code in Restricted Mode. Some language features may be disabled, but text editing is always supported.
Where did my installed extensions go?
In Restricted Mode, any extension that doesn't support Workspace Trust will be disabled, and all UI elements such as Activity bar icons and commands will not be displayed.
You can override an extension's Workspace Trust support level with the extensions.supportUntrustedWorkspaces setting but do so with care. Enabling extensions has more details.
Can I disable the Workspace Trust feature?
You can but it is not recommended. If you don't want VS Code to check for Workspace Trust when opening a new folder or repository, you can set security.workspace.trust.enabled to false. VS Code will then behave as it did before the 1.57 release.
How do I untrust a folder/workspace?
Bring up Workspace Trust editor (Workspaces: Manage Workspace Trust from the Command Palette) and select the Don't Trust button. You can also remove the folder from the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list.
Why don't I see the "Don't Trust" button?
If you don't see the Don't Trust button in the Workspace Trust dialog, the folder's trust level may be inherited from a parent folder. Review the Trusted Folders & Workspaces list to check if a parent folder has enabled Workspace Trust.
Some workflows such as connecting to a GitHub Codespace or attaching to a running Docker container are automatically trusted since these are managed environments to which you should already have a high level of trust.
What does Workspace Trust protect against?
Many features of VS Code allow third-party tools and extensions to run automatically, such as linting or format on save, or when you do certain operations like compiling code or debugging. An unethical person could craft an innocent looking project that would run malicious code without your knowledge and harm your local machine. Workspace Trust provides an extra layer of security by trying to prevent code execution while you are evaluating the safety and integrity of unfamiliar source code.