GitHub Copilot in VS Code
GitHub Copilot adds multi-agent development capabilities to Visual Studio Code. Plan your approach, then let AI agents implement and verify code changes across your project. Run multiple agent sessions in parallel: locally, in the background, or in the cloud. Manage them all from a central view. Inline suggestions, inline chat, and smart actions assist you throughout the rest of the coding workflow.
Agents and agent sessions
Agents handle complete coding tasks end-to-end. Give an agent a high-level task and it breaks the work into steps, edits files, runs terminal commands, invokes tools, and self-corrects when it hits errors or failing tests. Each task runs inside an agent session, a persistent conversation you can track, pause, resume, or hand off to another agent.
Your organization might have disabled agents in VS Code. Contact your admin to enable this functionality.
Manage sessions from a central view
Run multiple agent sessions in parallel, each focused on a different task. The Sessions view in the Chat panel gives you a single place to monitor all active sessions, whether they run locally, in the background, or in the cloud. See the status of each session, switch between them, review file changes, and pick up where you left off.
Learn more about managing agent sessions.
Run agents anywhere
Agents can run locally in VS Code for interactive work, in the background on your machine for autonomous tasks, or in the cloud for team collaboration via pull requests. You can also use third-party agents from providers like Anthropic and OpenAI. At any point, hand off a task from one agent type to another and the full conversation history carries over.
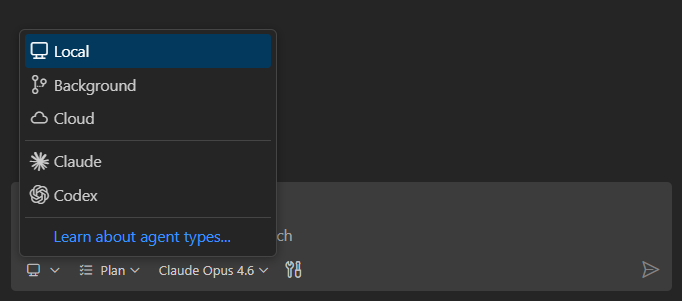
Learn more about agent types and delegation or follow the agents tutorial.
Plan before you build
Use the built-in Plan agent to break a task into a structured implementation plan before writing any code. The Plan agent analyzes your codebase, asks clarifying questions, and produces a step-by-step plan. When the plan looks right, hand it off to an implementation agent to execute it, locally, in the background, or in the cloud.
Learn more about planning with agents.
What can you do
-
Build a feature end-to-end. Describe a feature in natural language and the agent scaffolds the project, implements the logic across multiple files, and runs tests to verify the result.
-
Debug and fix failing tests. Point an agent at a failing test and it reads the error, traces the root cause across your codebase, applies a fix, and re-runs the test to confirm. Learn more about debugging with AI.
-
Refactor or migrate a codebase. Ask an agent to plan a migration, for example, from one framework to another, and it applies coordinated changes across files while verifying with builds.
-
Collaborate via pull requests. Delegate a task to a cloud agent that creates a branch, implements the changes, and opens a pull request for your team to review. Learn more about cloud agents.
Getting started
Step 1: Set up Copilot
-
Hover over the Copilot icon in the Status Bar and select Set up Copilot.

-
Choose a sign-in method and follow the prompts. If you don't have a Copilot subscription yet, you are signed up for the Copilot Free plan.
Step 2: Start your first agent session
-
Open the Chat view (⌃⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Alt+I)).
-
Enter a prompt that describes what you want to build, for example:
Create a basic Node.js web app for sharing recipes. Make it look modern and responsive. -
Review the generated code. The agent creates files, installs dependencies, and runs commands as needed.
-
Enter
/initto configure your project for AI. This creates custom instructions that help the agent understand your codebase and generate better code.
For a full hands-on tutorial covering inline suggestions, agents, inline chat, and customization, see Get started with GitHub Copilot in VS Code.
More ways to code with AI
Inline suggestions
Copilot provides code suggestions as you type, from single-line completions to full function implementations. Next edit suggestions predict the next logical change based on your current edits.
Learn more about inline suggestions in VS Code.
Inline chat
Press ⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+I) to open a chat prompt directly in the editor. Describe a change, and Copilot suggests edits in place, so you stay in the flow of coding. Use it for targeted refactors, explanations, or quick fixes without switching context.
Learn more about inline chat in VS Code.
Smart actions
VS Code includes predefined AI-powered actions for common tasks: generating commit messages, renaming symbols, fixing errors, and running semantic search across your project.
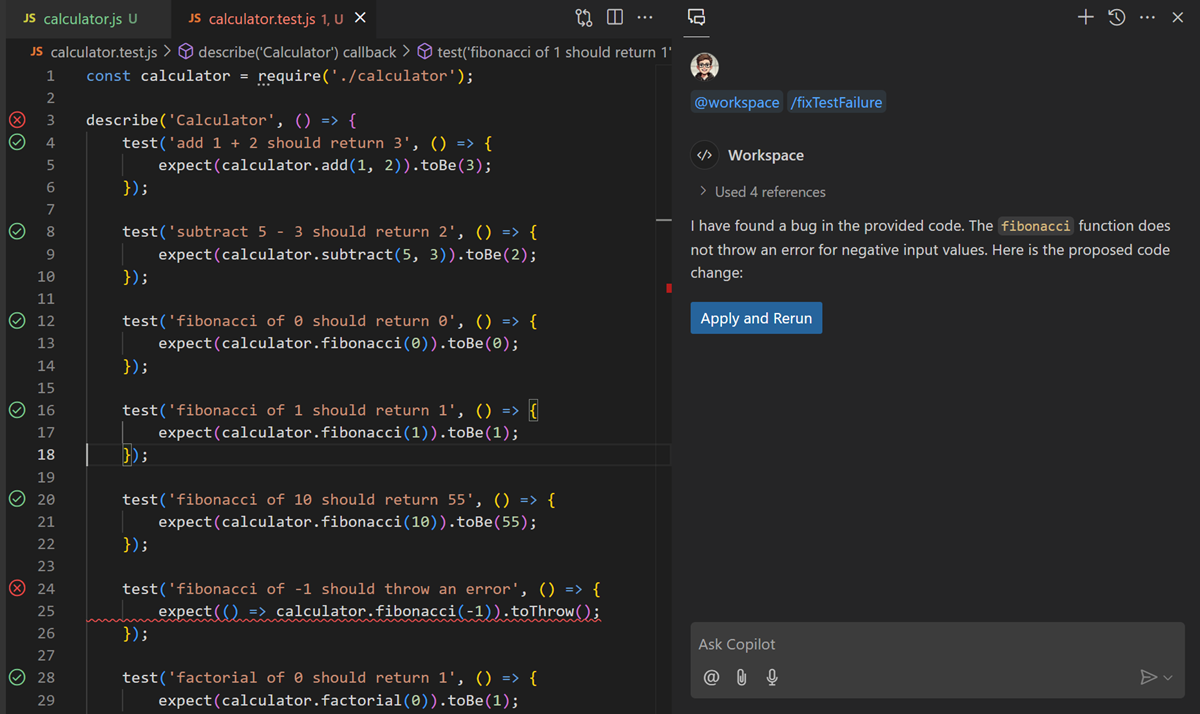
Learn more about smart actions in VS Code.
Customize AI for your workflow
Agents work best when they understand your project's conventions, have the right tools, and use a model suited to the task. VS Code gives you several ways to tailor the AI so it produces code that fits your codebase from the start, instead of requiring manual corrections after the fact.
- Custom instructions: Define project-wide coding conventions so the AI generates code that matches your style.
- Agent skills: Teach Copilot specialized capabilities that work across VS Code, GitHub Copilot CLI, and GitHub Copilot coding agent.
- Custom agents: Create agents that assume a specific role, such as a code reviewer or documentation writer, with their own tools and instructions.
- MCP servers: Extend agents with tools from MCP servers or Marketplace extensions.
- Hooks: Execute custom commands at specific events for automation and policy enforcement.
Support
Support for GitHub Copilot Chat is provided by GitHub and can be reached at https://support.github.com.
To learn more about Copilot's security, privacy, compliance, and transparency, see the GitHub Copilot Trust Center FAQ.
Pricing
You can start using GitHub Copilot for free with monthly limits on inline suggestions and chat interactions. For more extensive usage, you can choose from various paid plans.
View detailed GitHub Copilot pricing