Use MCP servers in VS Code
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that lets AI models use external tools and services through a unified interface. In VS Code, MCP servers provide tools for tasks like file operations, databases, or interacting with external APIs.
MCP servers are one of three ways to extend chat with tools in VS Code, alongside built-in tools and extension-contributed tools. Learn more about types of tools.
This article guides you through setting up MCP servers and using their capabilities in Visual Studio Code.
Your organization might have disabled the use of MCP servers in VS Code or restricted which MCP servers you can use. Contact your admin for more information.
How does MCP work?
MCP follows a client-server architecture:
- MCP clients (like VS Code) connect to MCP servers and request actions on behalf of the AI model
- MCP servers provide one or more tools that expose specific functionalities through a well-defined interface
- Model Context Protocol defines the message format for communication between clients and servers, including tool discovery, invocation, and response handling
For example, a file system MCP server might provide tools for reading, writing, or searching files and directories. GitHub's MCP server offers tools to list repositories, create pull requests, or manage issues. MCP servers can run locally on your machine or be hosted remotely, and VS Code supports both configurations.
By standardizing this interaction, MCP eliminates the need for custom integrations between each AI model and each tool. This allows you to extend your AI assistant's capabilities by simply adding new MCP servers to your workspace. Learn more about the Model Context Protocol specification.
Supported MCP capabilities in VS Code
VS Code supports the following MCP capabilities:
-
- Local standard input/output (
stdio) - Streamable HTTP (
http) - Server-sent events (
sse) - legacy support.
- Local standard input/output (
-
- Tools
- Prompts
- Resources
- Elicitation
- Sampling
- Authentication
- Server instructions
- Roots
MCP support in VS Code is generally available starting from VS Code 1.102.
Prerequisites
- Install the latest version of Visual Studio Code
- Access to Copilot
Add an MCP server
Local MCP servers can run arbitrary code on your machine. Only add servers from trusted sources, and review the publisher and server configuration before starting it. VS Code prompts you to confirm that you trust the MCP server when you start an MCP server for the first time. Read the Security documentation for using AI in VS Code to understand the implications.
Add an MCP server from the GitHub MCP server registry
You can install an MCP server directly from the GitHub MCP server registry via the Extensions view in VS Code. You can choose to install the MCP server either in your user profile or in the current workspace.
To install an MCP server from the Extensions view:
-
Enable the MCP server gallery with the
chat.mcp.gallery.enabledsetting. -
Open the Extensions view (⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X))
-
Enter
@mcpin the search field to show the list of MCP servers or run the MCP: Browse Servers command from the Command Palette.VS Code retrieves the list of MCP servers from the GitHub MCP server registry.
-
To install an MCP server:
-
In your user profile: select Install
-
In your workspace: right-click the MCP server and select Install in Workspace
-
-
To view the MCP server details, select the MCP server in the list.
Other options to add an MCP server
You have several other options to add an MCP server in VS Code:
Add an MCP server to a workspace `mcp.json` file
If you want to configure MCP servers for a specific project, you can add the server configuration to your workspace in the .vscode/mcp.json file. This allows you to share the same MCP server configuration with your project team.
Make sure to avoid hardcoding sensitive information like API keys and other credentials by using input variables or environment files.
To add an MCP server to your workspace:
-
Create a
.vscode/mcp.jsonfile in your workspace. -
Select the Add Server button in the editor to add a template for a new server. VS Code provides IntelliSense for the MCP server configuration file.
The following example shows how to configure the GitHub remote MCP server. Learn more about the MCP configuration format in VS Code.
{ "servers": { "github-mcp": { "type": "http", "url": "https://api.githubcopilot.com/mcp" } } } -
Alternatively, run the MCP: Add Server command from the Command Palette, choose the type of MCP server to add and provide the server information. Next, select Workspace to add the server to the
.vscode/mcp.jsonfile in your workspace.
Add an MCP server to your user configuration
To configure an MCP server for all your workspaces, you can add the server configuration to your user profile. This enables you to reuse the same server configuration across multiple projects.
To add an MCP server to your user configuration:
-
Run the MCP: Add Server command from the Command Palette, provide the server information, and then select Global to add the server configuration to your profile.
-
Alternatively, run the MCP: Open User Configuration command, which opens the
mcp.jsonfile in your user profile. You can then manually add the server configuration to the file.
When you use multiple VS Code profiles, this allows you to switch between different MCP server configurations based on your active profile. For example, the Playwright MCP server could be configured in a web development profile, but not in a Python development profile.
MCP servers are executed wherever they're configured. If you're connected to a remote and want a server to run on the remote machine, it should be defined in your remote settings (MCP: Open Remote User Configuration) or in the workspace's settings. MCP servers defined in your user settings are always executed locally.
Add an MCP server to a dev container
MCP servers can be configured in Dev Containers through the devcontainer.json file. This allows you to include MCP server configurations as part of your containerized development environment.
To configure MCP servers in a Dev Container, add the server configuration to the customizations.vscode.mcp section:
{
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/devcontainers/typescript-node:latest",
"customizations": {
"vscode": {
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"playwright": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@microsoft/mcp-server-playwright"]
}
}
}
}
}
}
When the Dev Container is created, VS Code automatically writes the MCP server configurations to the remote mcp.json file, making them available in your containerized development environment.
Automatically discover MCP servers
VS Code can automatically detect and reuse MCP server configurations from other applications, such as Claude Desktop.
Configure autodiscovery with the
Install an MCP server from the command line
You can also use the VS Code command-line interface to add an MCP server to your user profile or to a workspace.
To add an MCP server to your user profile, use the --add-mcp VS Code command line option, and provide the JSON server configuration in the form {\"name\":\"server-name\",\"command\":...}.
code --add-mcp "{\"name\":\"my-server\",\"command\": \"uvx\",\"args\": [\"mcp-server-fetch\"]}"
Use MCP tools in chat
Once you have added an MCP server, you can use the tools it provides in chat. MCP tools work like other tools in VS Code: they can be automatically invoked when using agents or explicitly referenced in your prompts.
To use MCP tools in chat:
-
Open the Chat view (⌃⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Alt+I)).
-
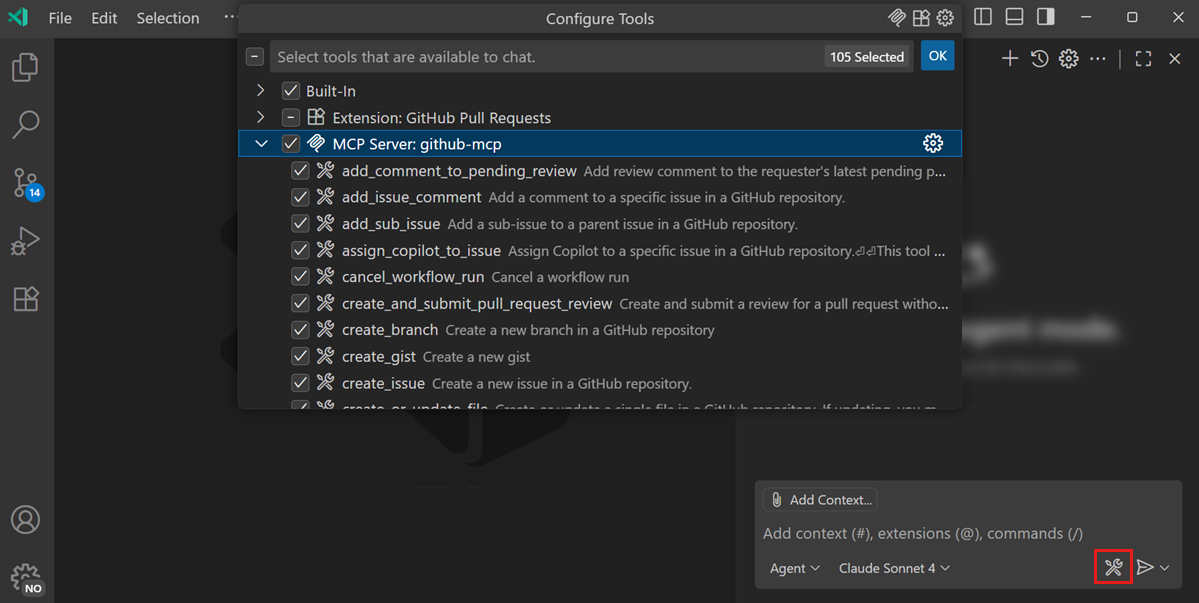
Open the tool picker to select which tools the agent is allowed to use. MCP tools are grouped per MCP server.
TipWhen you create custom prompts or custom agents, you can also specify which MCP tools can be used.
-
When using agents, tools are automatically invoked as needed based on your prompt.
For example, install the GitHub MCP server and then ask "List my GitHub issues".
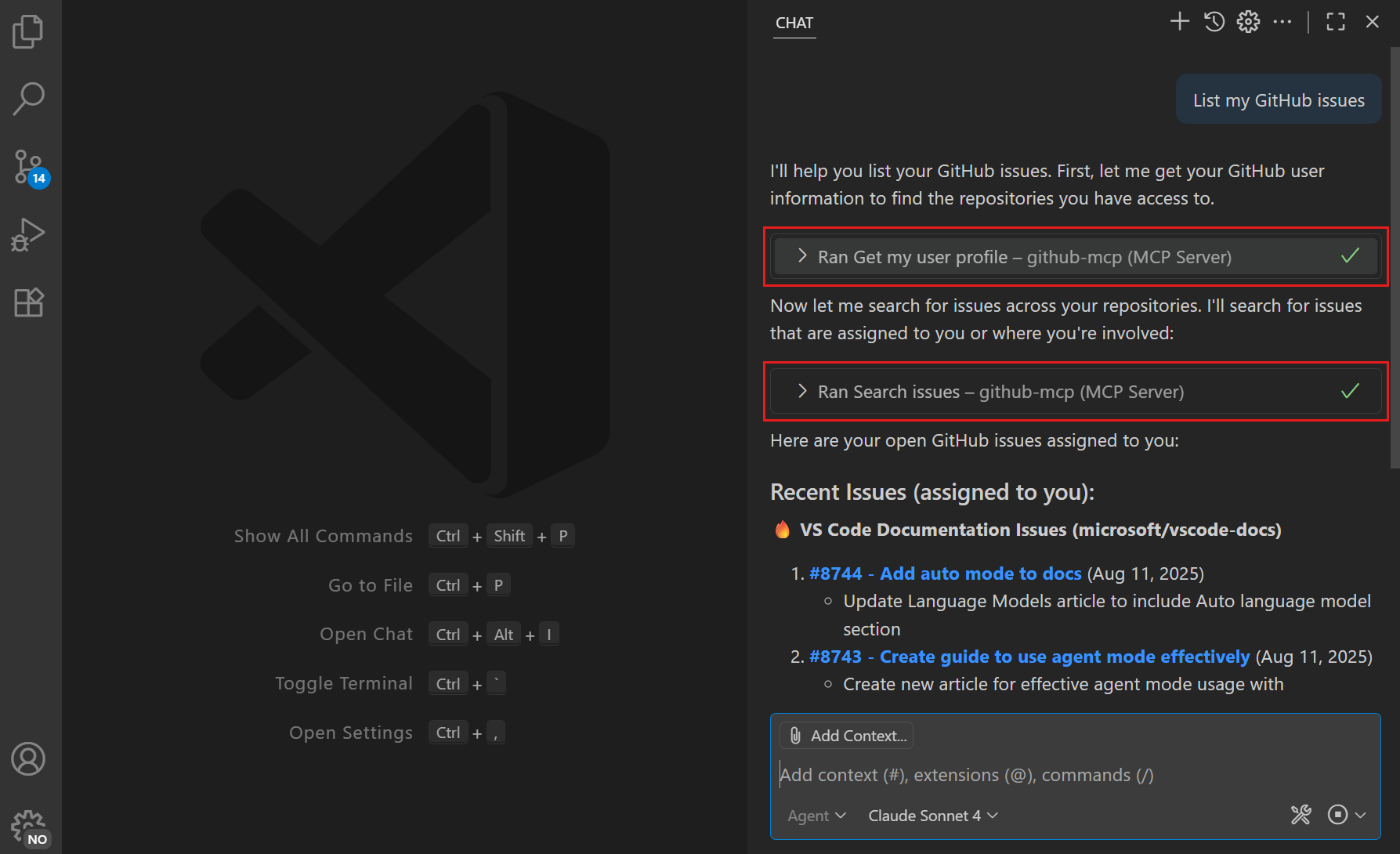
-
You can also explicitly reference MCP tools by typing
#followed by the tool name. -
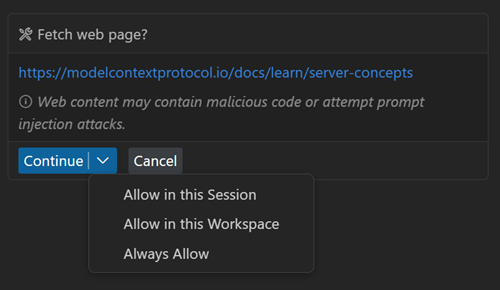
Review and approve tool invocations when prompted.
Learn more about using tools in chat, including how to manage tool approvals, use the tool picker, and create tool sets.
Clear cached MCP tools
When VS Code starts the MCP server for the first time, it discovers the server's capabilities and tools. You can then use these tools in chat. VS Code caches the list of tools for an MCP server. To clear the cached tools, use the MCP: Reset Cached Tools command in the Command Palette.
Use MCP resources
MCP servers can give direct access to resources that you can use as context in your chat prompts. For example, a file system MCP server can let you access files and directories, or a database MCP server might provide access to database tables.
To add a resource from an MCP server to your chat prompt:
-
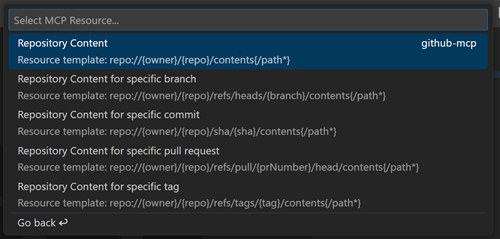
In the Chat view, select Add Context > MCP Resources
-
Select a resource type from the list and provide optional resource input parameters.
To view the list of available resources for an MCP server, use the MCP: Browse Resources command or use the MCP: List Servers > Browse Resources command to view resources for a specific server.
MCP tools can return resources as part of their response. You can view or save these resources to your workspace by selecting Save or by dragging and dropping the resource to the Explorer view.
Use MCP prompts
MCP servers can provide preconfigured prompts for common tasks that you can invoke in chat with a slash command. To invoke an MCP prompt in chat, type / in the chat input field, followed by the prompt name, formatted as mcp.servername.promptname.
Optionally, the MCP prompt might ask you for extra input parameters.
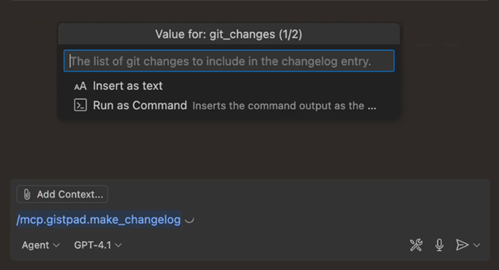
Group related tools in a tool set
As you add more MCP servers, the list of tools can become long. You can group related tools into a tool set to make them easier to manage and reference.
Learn more about how to create and use tool sets.
Manage installed MCP servers
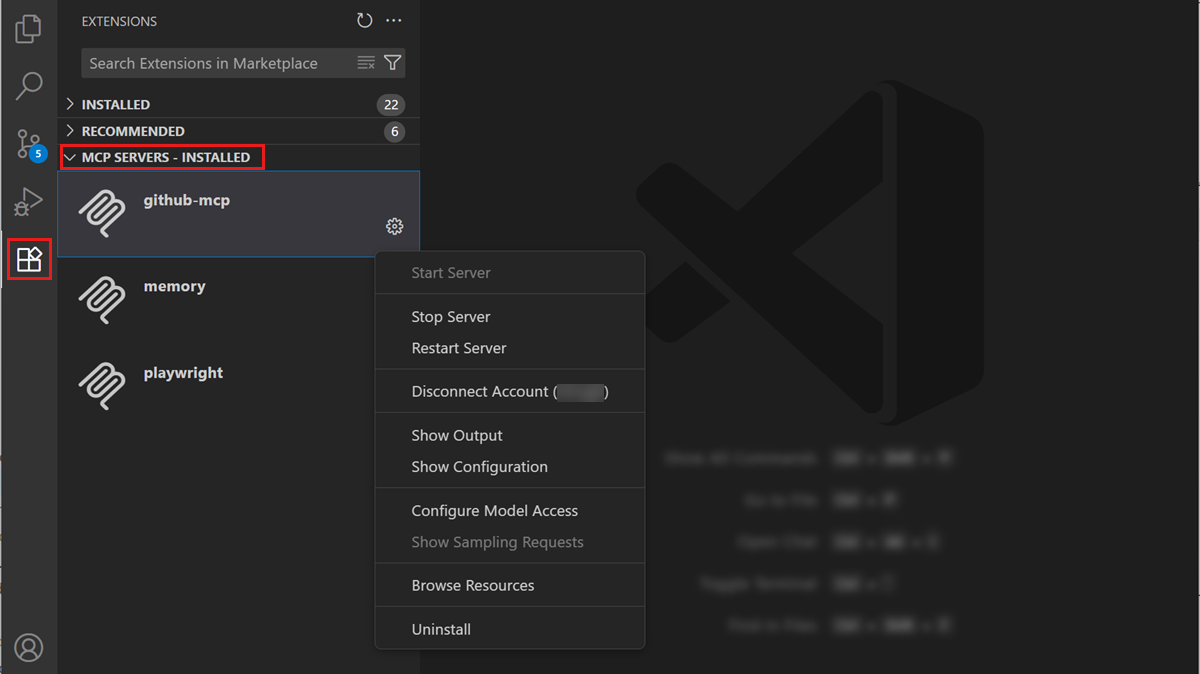
You can perform various actions on the installed MCP servers, such as starting or stopping a server, viewing the server logs, uninstalling the server, and more.
To perform these actions on an MCP server, use either of these options:
-
Right-click a server in the MCP SERVERS - INSTALLED section or select the gear icon
-
Open the
mcp.jsonconfiguration file and access the actions inline in the editor (code lenses)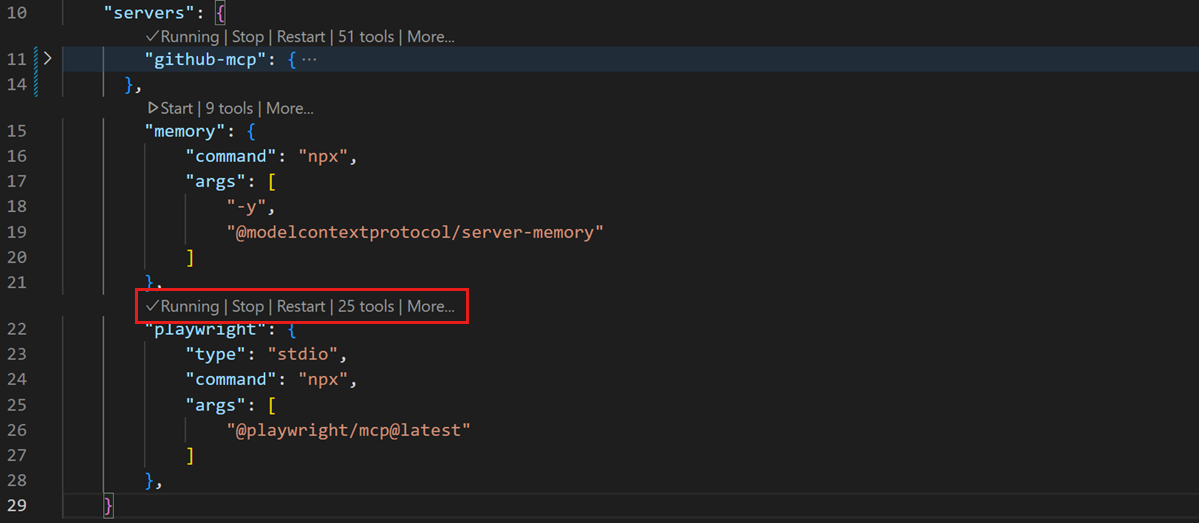
Use the MCP: Open User Configuration or MCP: Open Workspace Folder Configuration commands to access the MCP server configuration.
-
Run the MCP: List Servers command from the Command Palette and select a server
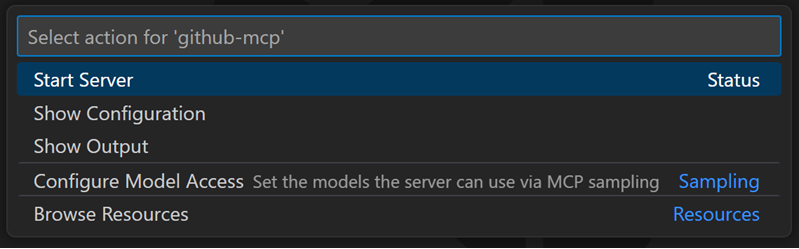
Automatically start MCP servers
When you add an MCP server or change its configuration, VS Code needs to (re)start the server to discover the tools it provides.
You can configure VS Code to automatically restart the MCP server when configuration changes are detected by using the
Alternatively, manually restart the MCP server from the Chat view, or by selecting the restart action from the MCP server list.
Find MCP servers
MCP is still a relatively new standard, and the ecosystem is rapidly evolving. As more developers adopt MCP, you can expect to see an increasing number of servers and tools available for integration with your projects.
The GitHub MCP server registry is a great starting point. You can access the registry directly from the Extensions view in VS Code.
MCP's official server repository provides official, and community-contributed servers that showcase MCP's versatility. You can explore servers for various functionalities, such as file system operations, database interactions, and web services.
VS Code extensions can also contribute MCP servers and configure them as part of the extension's installation process. Check the Visual Studio Marketplace for extensions that provide MCP server support.
MCP server trust
MCP servers can run arbitrary code on your machine. Only add servers from trusted sources, and review the publisher and server configuration before starting it. Read the Security documentation for using AI in VS Code to understand the implications.
When you add an MCP server to your workspace or change its configuration, you need to confirm that you trust the server and its capabilities before starting it. VS Code shows a dialog to confirm that you trust the server when you start a server for the first time. Select the link to MCP server in the dialog to review the MCP server configuration in a separate window.
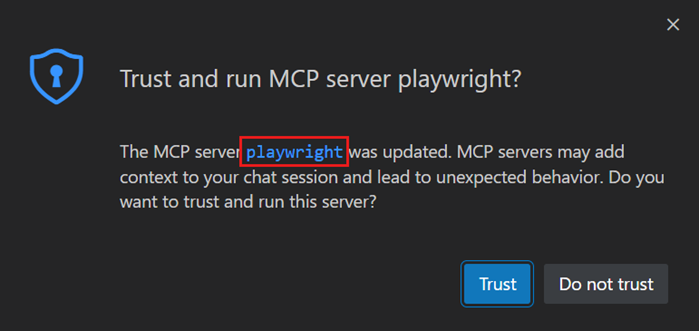
If you don't trust the server, it is not started, and chat requests continue without using the tools provided by the server.
You can reset trust for your MCP servers by running the MCP: Reset Trust command from the Command Palette.
If you start the MCP server directly from the mcp.json file, you are not prompted to trust the server configuration.
Synchronize MCP servers across devices
With Settings Sync enabled, you can synchronize settings and configurations across devices, including MCP server configurations. This allows you to maintain a consistent development environment and access the same MCP servers on all your devices.
To enable MCP server synchronization with Settings Sync, run the Settings Sync: Configure command from the Command Palette, and ensure that MCP Servers is included in the list of synchronized configurations.
Configuration format
MCP servers are configured using a JSON file (mcp.json) that defines two main sections: server definitions and optional input variables for sensitive data.
MCP servers can connect using different transport methods. Choose the appropriate configuration based on how your server communicates.
Configuration structure
The configuration file has two main sections:
"servers": {}- Contains the list of MCP servers and their configurations"inputs": []- Optional placeholders for sensitive information like API keys
You can use predefined variables in the server configuration, for example to refer to the workspace folder (${workspaceFolder}).
Standard I/O (stdio) servers
Use this configuration for servers that communicate through standard input and output streams. This is the most common type for locally-run MCP servers.
| Field | Required | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
Yes | Server connection type | "stdio" |
command |
Yes | Command to start the server executable. Must be available on your system path or contain its full path. | "npx", "node", "python", "docker" |
args |
No | Array of arguments passed to the command | ["server.py", "--port", "3000"] |
env |
No | Environment variables for the server | {"API_KEY": "${input:api-key}"} |
envFile |
No | Path to an environment file to load more variables | "${workspaceFolder}/.env" |
When using Docker with stdio servers, don't use the detach option (-d). The server must run in the foreground to communicate with VS Code.
Example local server configuration
This example shows the minimal configuration for a basic, local MCP server using npx:
{
"servers": {
"memory": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@modelcontextprotocol/server-memory"]
}
}
}
HTTP and Server-Sent Events (SSE) servers
Use this configuration for servers that communicate over HTTP. VS Code first tries the HTTP Stream transport and falls back to SSE if HTTP is not supported.
| Field | Required | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
Yes | Server connection type | "http", "sse" |
url |
Yes | URL of the server | "http://localhost:3000", "https://api.example.com/mcp" |
headers |
No | HTTP headers for authentication or configuration | {"Authorization": "Bearer ${input:api-token}"} |
In addition to servers available over the network, VS Code can connect to MCP servers listening for HTTP traffic on Unix sockets or Windows named pipes by specifying the socket or pipe path in the form unix:///path/to/server.sock or pipe:///pipe/named-pipe on Windows. You can specify subpaths by using a URL fragment, such as unix:///tmp/server.sock#/mcp/subpath.
Example remote server configuration
This example shows the minimal configuration for a remote MCP server without authentication:
{
"servers": {
"context7": {
"type": "http",
"url": "https://mcp.context7.com/mcp"
}
}
}
Input variables for sensitive data
Input variables let you define placeholders for configuration values, avoiding the need to hardcode sensitive information like API keys or passwords directly in the server configuration.
When you reference an input variable using ${input:variable-id}, VS Code prompts you for the value when the server starts for the first time. The value is then securely stored for subsequent use. Learn more about input variables in VS Code.
Input variable properties:
| Field | Required | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
type |
Yes | Type of input prompt | "promptString" |
id |
Yes | Unique identifier to reference in server config | "api-key", "database-url" |
description |
Yes | User-friendly prompt text | "GitHub Personal Access Token" |
password |
No | Hide typed input (default: false) | true for API keys and passwords |
Example server configuration with input variables
This example configures a local server that requires an API key:
{
"inputs": [
{
"type": "promptString",
"id": "perplexity-key",
"description": "Perplexity API Key",
"password": true
}
],
"servers": {
"perplexity": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "server-perplexity-ask"],
"env": {
"PERPLEXITY_API_KEY": "${input:perplexity-key}"
}
}
}
}
Server naming conventions
When defining MCP servers, follow these naming conventions for the server name:
- Use camelCase for the server name, such as "uiTesting" or "githubIntegration"
- Avoid using whitespace or special characters
- Use a unique name for each server to avoid conflicts
- Use a descriptive name that reflects the server's functionality or brand, such as "github" or "database"
Troubleshoot and debug MCP servers
MCP output log
When VS Code encounters an issue with an MCP server, it shows an error indicator in the Chat view.
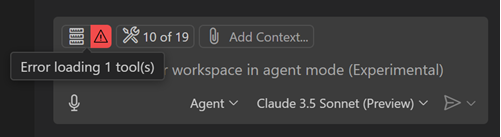
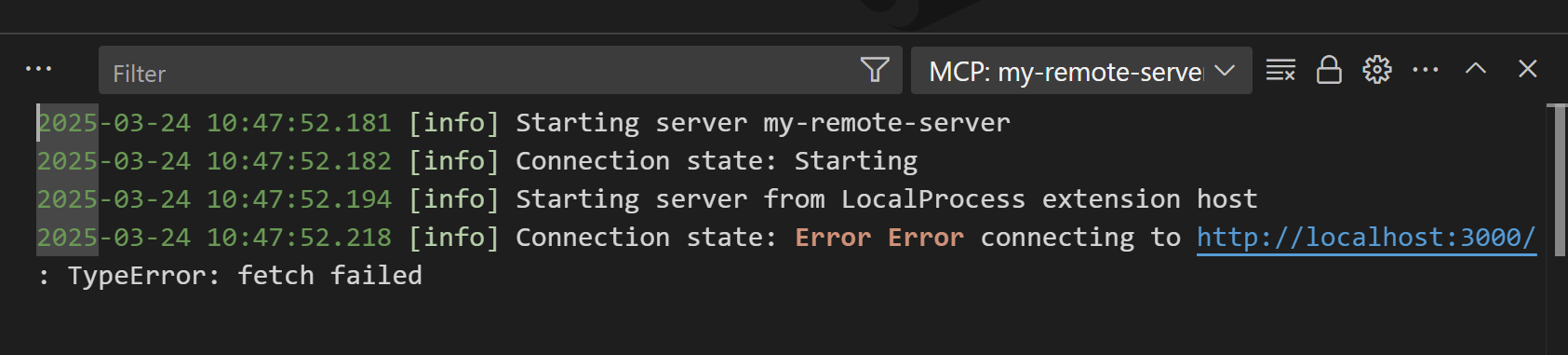
Select the error notification in the Chat view, and then select the Show Output option to view the server logs. Alternatively, run MCP: List Servers from the Command Palette, select the server, and then choose Show Output.
Debug an MCP server
You can enable development mode for MCP servers by adding a dev key to the MCP server configuration. This is an object with two properties:
watch: A file glob pattern to watch for files change that will restart the MCP server.debug: Enables you to set up a debugger with the MCP server. Currently, VS Code supports debugging Node.js and Python MCP servers.
Learn more about MCP development mode in the MCP Dev Guide.
Centrally control MCP access
Organizations can centrally manage access to MCP servers via GitHub policies. Learn more about enterprise management of MCP servers.
Frequently asked questions
Can I control which MCP tools are used?
- Select the Tools button in the Chat view when using agents, and toggle specific tools on/off as needed.
- Add specific tools to your prompt by using the Add Context button or by typing
#. - For more advanced control, you can use
.github/copilot-instructions.mdto fine-tune tool usage.
The MCP server is not starting when using Docker
Verify that the command arguments are correct and that the container is not running in detached mode (-d option). You can also check the MCP server output for any error messages (see Troubleshooting).
I'm getting an error that says "Cannot have more than 128 tools per request."
A chat request can have a maximum of 128 tools enabled at a time due to model constraints. If you have more than 128 tools selected, reduce the number of tools by deselecting some tools or whole servers in the tools picker in the Chat view, or ensure that virtual tools are enabled (